Today one of the most popular types of energy replenishment household appliances are nickel-cadmium batteries. This is a fairly easy-to-use device that, if handled correctly, will last a fairly long period of time. How to properly handle nickel-cadmium batteries should be considered in more detail.
general characteristics
The nickel-cadmium battery is designed in such a way that at low internal resistance he can give enough high current. Such batteries can withstand even short circuits.
Batteries of the presented type can easily withstand long-term loads. When the ambient temperature drops, their performance remains virtually unchanged.
Nickel-cadmium batteries inferior to other species in capacity. However, their high efficiency makes batteries one of the most popular and in demand in the field of portable technology.
For devices with electric motors that consume high currents, the use of chargers such as nickel-cadmium batteries is simply irreplaceable.
The discharge currents at which they are used are in the range of 20-40 A. Load limit for NiCd batteries is 70 A.
Advantages
The presented devices have a number of advantages. They are able to work in wide range discharge and charge currents, as well as temperature.

Nickel-cadmium batteries can be charged when low temperatures, which is explained by the high load capacity. They are not picky about the type of tightening device. This significant advantage. It sets the device apart from the mass of other varieties, since the nickel-cadmium battery can be charged in any conditions. It is resistant to mechanical stress and fireproof. Nickel-cadmium batteries have more than 1000 charge cycles and have the ability to recover after a decrease in capacity.
Low cost along with the listed advantages make NiCd batteries very popular.
Flaws
The nickel-cadmium battery design also has a number of disadvantages. The main one is the “memory effect”.

Over the course of several charge-discharge cycles, the structure of the electrode surface changes. In this case, the separator forms chemical compounds, which will subsequently interfere with discharge with low currents. This leads to the source remembering its incomplete discharge.
The further you charge nickel-cadmium batteries, the more they will lose their efficiency. The source will have less and less capacity.
A disadvantage is also the high self-discharge during the first day, up to 10% after charging. Large dimensions can also be considered a disadvantage.
Charger
To understand how to charge nickel-cadmium batteries, you should consider a number of features of this process.

Fast charging mode for the presented power sources is preferable to slow charging. Pulse replenishment of capacity is better for them than direct current.
It is recommended to restore the device. Nickel-cadmium batteries require this. Manufacturers of the corresponding devices have taken into account how to charge them using this method. Reversible charging speeds up the process due to the recombination of gases released during the process.
The presented technique for restoring such batteries allows increasing the service life by up to 15%. How to charge a nickel-cadmium battery? There is a whole technology. To increase efficiency, some users use fast charging followed by refueling with weak currents. This allows the battery to be filled more tightly.
Storage and disposal
The batteries shown should be stored in a discharged state. There are chargers that have a discharge function. If this is not available, before storage, nickel-cadmium batteries are emptied using an incandescent lamp with permissible current 3-20 A. Connect the battery to it and wait until the spiral begins to turn red.
This procedure will allow you to store the device for quite a long time. Moreover, environmental conditions and temperature changes will not have an impact on the device.
If you need to dispose of this type of battery, you should take it to a special collection point for such devices. All developed countries have them. This is due to the presence of cadmium in the battery. Its toxicity is comparable to mercury.
Understanding the technology of how to charge a nickel-cadmium battery, store it and dispose of it, there is no doubt about the safety and durability of this power source. It will not harm the environment and human health if batteries are disposed of responsibly.
Recovery
Nickel-cadmium batteries are the only type of such devices that require restoration.

Periodic discharge-charge cycle will increase the life of the batteries. This should not be done too often, but from time to time it is simply necessary.
There are two types of devices for recovery. The first is called a reverse pulse charger with different duration times. This is very efficient device, but complex and expensive. Remanufacturing of nickel-cadmium batteries can be carried out in less than simple device. It performs a discharge-charge cycle automatically. This device is cheaper, more convenient and allows you to charge 2-4 batteries at once.
To carry out the process, you need to insert batteries into the equipment cassette. The number of batteries is set using the switch. Plugging the device into the network will activate the indicator. Red indicates charging and yellow indicates discharging. Green light notification indicator about process termination. Batteries must be discharged forcibly. To do this, you need to switch a certain lever on the device. After the discharge is completed, the device will continue the charging process automatically.
Having become familiar with the basic characteristics of a power source such as nickel-cadmium batteries, you can use them correctly. By following the manufacturer's instructions and regularly reconditioning your batteries, you can significantly extend their life. By correctly disposing of the presented device, it will be quite simple to protect yourself, other people and the environment as a whole from the toxic effects of cadmium.
The channel nespokoyniy told how to restore a dead battery, which is installed on a screwdriver. In our case, a nickel-cadmium battery. You can buy everything you need for restoration from free shipping in this Chinese store.
I took apart the boxes. This is what they look like.
I decided to restore it because there is no charge in the nickel-cadmium battery. The reason is that several cans do not gain capacity and, accordingly, the entire battery does not accept a charge, there is no work. The battery has 1300 capacity. I tried to charge one jar at a time with this device, one at a time. I looked at how much each one was charging. IN in this case, if the top bank was signed 1781, 1888, this is despite the fact that the norm is 1300 written. Some are 68, 73, 50, others are normal 1340, 1359. Some are normal, some do not take a charge.
Battery or any source of approximately 12 volts. I tied 2 wires, plus or minus, on my knees and did the so-called battery start. We touch the wires to the jar, which is 1.2 volts. There is a small click, for one second, remove it. We do this 3-4 times.
After that, we begin to charge in a new way from the IMAX B6. IN this moment charging is in progress. Apparently I already scored 1382 in about 1.5 hours. 1383, 1.76 volts, the processor decides how much voltage to give. First we program, then we set. One 1.2 volt bank, charging. The one who scored 1387 doesn't take any more. Initially, 71 are provided. Already, roughly speaking, 1400. After such a start, a short touch with a powerful voltage, almost 10 times. Also, let’s not move here, the crocodiles might get unstuck. There was also a bank, 40 was indicated, 1426 was dialed and the like, the bank was 80-something, that is, everyone is dialing more than 1300. Thus, the plan is to drive it away. There are still a couple of jars left to make for this battery.
Continuation from 4 minutes on the video about the method of restoring a nickel-cadmium battery that has failed.
There is a way.
Three ways to repair a screwdriver battery
If your screwdriver battery is broken, there are several ways to fix it. 
1. Replace the “dead” can.
Let's look at this method using the example of a 12 V, NiCd (nickel-cadmium battery) screwdriver. Its battery inside has 10 1.2 volt cells connected in series, which gives us 12 volts at the output (1.2*10=12). The capacity of all cans is the same, for example 1.5 Ah. 
When the cans are connected in series, we have the same 1.5 Ah at the output. We measure the voltage on each bank with a voltmeter. Usually the battery fails due to one cell. The “dead” can will have the lowest voltage.

It needs to be replaced with another one. Where can I get it? If you have two “dead” batteries, then you can make one out of two. You can ask your friends; many have old Shuriki cars in the garage. You can order a jar in China. The main thing is that the element (can) is completely identical in voltage and capacity to the rest of the battery elements. You need to buy cans with already welded plates, since it is not advisable to solder the cans themselves. We solder the plates together for both old and new elements.

2. Completely replace all elements
3. Convert the battery to lithium ion
You need to purchase high-current lithium banks of the required capacity and a BMS balancing board to charge them in China. You can also buy a connector and charger for these cans. But you can charge it with standard charging. You can read more about this modification on my channel.
https://zen.yandex.ru/media/master_dom/
Makita screwdriver battery repair
Hello dear readers. A friend of mine has a good screwdriver, Makita 6271. “Shurik” is cool, although old, but the batteries have long since died. He asked me to convert the batteries to lithium ion ones. I ordered all the components in China, waited for the parcels and started reworking.
Of the old “cans” you will only need the top two, on which the terminal block sits. 
We release the case and remove all the plastic protrusions in it. 
I decided to install 3 batteries, type 18650, a 20 A balancing board and a charging socket. High-current batteries are needed, with a discharge current of 20 or 30 A. 
I tied the batteries together with electrical tape and soldered them. You need to solder quickly without overheating the can. 
Then I soldered the necessary wires to the batteries, following the diagram on the board. 
The wires were initially taken longer than required. 
After soldering, I covered the contacts with double-sided tape. 
The socket, terminals and temperature sensor (TD) were connected as follows: 
The sensor itself looks something like this. It needs to be unsoldered from the negative terminal and soldered to the B- contact, which will allow you to charge the battery using native charging. 
Prepared a socket for the charger.

I assembled all the elements, soldered them according to the diagrams and closed the case.

I made a socket for a second charger just in case, the price of one socket is about 5 rubles.

If you buy a charger, it is better to buy one with these parameters. Everything works, the battery turned out to be very light. Good luck with your rework too.

The cadmium battery is a popular source of energy, which is used to complete household appliances.
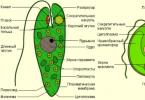
They are classified as alkaline types. They are equipped with those units and devices into which other models cannot be included. Nickel-cadmium batteries contain negative and positive conductive terminals, for the separation of which a separator is used. Interior
filled with alkaline electrolytic composition. The housing for nickel-cadmium batteries is prepared from a special metal and hermetically sealed. In order to ensure, to prepare the electrodes, foil is used, which is not very thick. To construct a separator, which is concentrated between the terminals in nickel-cadmium batteries, woven raw materials are used. After all, it does not interact with alkaline electrolyte.
Borne is used to connect the battery to other nickel-cadmium power sources. The nickel-cadmium battery design includes welded joints to ensure a tight connection.
Advantages of Nickel Cadmium Power Supply
- The number of discharge and charge cycles reaches 1,000 or more.
- The storage period for such devices is long. At the same time, the degree of charge of the unit does not affect this indicator.
- The technology for charging nickel-cadmium batteries is relatively simple. Novice motorists can also implement it.
- Such power supplies can also be used in winter period, in harsh conditions.
- The capacity does not decrease even at sub-zero temperatures.

Negative sides
- The devices have a property called a “memory effect”. To eliminate it, there is a need to carry out certain measures.
- The level of self-discharge is increased.
- If you compare CD batteries with other power sources, you can highlight their low energy density.
- Toxic components were used for preparation. Therefore, some states do not use such rechargeable batteries, do not manufacture them.
- To dispose of such units, appropriate equipment is used. In our country, installations for recycling and recycling are being prepared for nickel-cadmium units.
Charge and discharge of nickel-cadmium batteries
Discharge process
The discharge parameters of the power source largely depend on design features, characteristics of electrodes and current leads. They also predetermine the magnitude of voltage and internal resistance.
Bit parameters depend on:
- Features and structures of the separator.
- Build quality.
- The amount of electrolytic composition with which the housing is filled.
- Other.
When discharging a nicd source for a long time, experts recommend using disk batteries, which are supplemented with large-sized pressed leads. Therefore, with a slight increase in current, the discharge capacity, as well as the voltage, decreases. In order to optimize this indicator, the thickness of the leads is reduced and the number is increased.
The maximum capacitance value is observed at room temperature. Further increase in temperature does not affect this parameter. Negative temperatures provoke a decrease in discharge voltage and an increase in discharge current.
The use of screwdrivers equipped with nickel-cadmium power supplies in winter requires caution.
Charging process
When charging ni cd batteries, it is necessary to introduce charge restrictions. After all, during the recharging process, the pressure inside the case increases, oxygen is produced, and the current application coefficient decreases.
How to charge ni cd battery? In order to fully restore the charge, a capacity of 150–160 percent must be provided. Temperature range – 0-+35 degrees. If you don't take into account temperature Range, then the pressure will increase. Through the emergency valve it will be released oxygen mixture. Therefore, it is important to determine in advance how to properly charge the battery.
A discharged nickel-cadmium battery is charged in various modes. The charging time depends on which mode is selected.
- Current of 0.2 of the total capacity for 7 hours.
- A current of 0.3 of the total capacity for no more than 4 hours.
When charging the unit in accelerated mode (with a current of 0.4 of the available capacity), overcharging is prohibited, as this will lead to a decrease in capacity. You can set how much the power source is charged using appropriate devices. When working with currents, an ammeter is used. To determine the number of volts, use a voltmeter or multimeter.

Charger for nickel-cadmium batteries
To charge ni cd batteries, reversible and automatic chargers are used.
Automatic Charger for ni cd is easy to use. With its help you can recharge 2–4 batteries for a screwdriver or other household appliances. After placing the battery in the memory, the mode and number are set. After this, the unit is connected to the network.
Automatic models are equipped with indicators that help determine the state of the charging power sources when working with current. Such devices are also suitable for discharging ni cd batteries.
Pulse chargers have a more complex design. They can be used when working with significant current. Since they are classified as professional units, before use you learn how to charge the power source and how to set the required parameters.
Reverse (pulse) models are suitable for cyclic supply of charge and discharge current. During discharge and charging, the parameters of current and voltage are determined in advance.
Features of use
Long-term operation affects the functioning and performance of cadmium-nickel batteries. Performance deterioration and failure are caused by:
- The working surface of the conductive terminals is reduced.
- The active mass of the conductive terminals is significantly reduced.
- The alkaline electrolytic composition changes composition and is incorrectly redistributed throughout the power source.
- Leakage occurs along conductive elements. As a result, the discharge of a charged power source occurs quite quickly.
- The consumption of liquid and oxygen increases. If oxygen is released excessively, the process becomes irreversible.
- Organic compounds begin to disintegrate.

Reconditioning of nickel-cadmium batteries
The restoration procedure for nickel-cadmium batteries, which are used to complete a screwdriver or other portable unit, takes some time. Since the cost of such batteries is high, the features should be studied before implementation.
Essentially, we restore the nickel-cadmium battery of the screwdriver with a pulsed current, which is supplied for 2-4 seconds. The current value exceeds the capacitance parameters by 10 or more times.
Before restoring the battery, certain elements and tools are prepared:
- Efficient power supply with strong current ratings. A car battery is used as a battery.
- Clamps.
- Wires.
- A multimeter that monitors voltage.
- Protective items.
The recovery procedure includes certain activities:
- The positive and negative terminals of a portable tool unit or a separate battery are determined.
- Using clamps or alligator clips, as well as pieces of wire, the cons are attached.
- The other end of the wire is pressed to the positive contact. The duration of wire contact is 1–2 seconds (can be increased to 3 seconds). Such actions take a little time. When making contact, make sure that the wires do not stick to the unit or battery.
After one cycle, the voltage level is measured using a multimeter. As soon as the voltage has been restored, they proceed to increasing the capacity. In order to restore and repair the power supply, 2–4 cycles are performed.
This technique brings the expected effect only on short term. This is because the electrolytic composition changes, and its volume also changes. As a result, batteries cannot be used as sources for a long time.

Modernized technique
In order to restore nickel-cadmium batteries with your own hands, as well as ensure their long-term operation, perform the following steps:
- All batteries are carefully checked and the voltage is measured. Those elements on which the voltage is close to zero are removed.
- Using an appropriate tool, holes are prepared in the body to fill 1 cm3 of distilled water.
- The power sources are allowed to settle for a short period of time, after which they are recheck voltage.
- If the functionality of the battery is restored, then the formed holes are treated with sealant and soldering.
- The unit is equipped with batteries and is rechargeable. The portable instrument is ready for use as soon as the indicator on the charger changes color. For these purposes, it is worth using pulse chargers, which are distinguished by extensive functionality and high-quality equipment.
- At zero voltage, distilled water is reintroduced into the battery.
- The procedure is repeated until a positive result is achieved.
Storage Features
Operating instructions for cadmium batteries have been prepared by specialists. The instructions describe how to store power supplies. Several basic rules have been highlighted.
Ni cd sources can only be stored when completely discharged. For these purposes, chargers that are equipped with the appropriate function are used. For emptying, incandescent lamps with the appropriate number of amperes are also used.
Batteries that are properly prepared can be stored for a long time. Temperature changes do not affect the condition and performance.
Premises are used to store nickel-cadmium batteries. After all, temperature fluctuations do not provoke discharge or the launch of irreversible processes.
Although nickel-cadmium batteries are stored for a long time, at a certain stage there is a need for disposal. To do this, you should contact an organization that performs similar processes.
The efficiency of nickel-cadmium batteries is difficult to overestimate. They are equipped with portable tools used in everyday life and in industry. With proper handling, compliance with safety precautions and operating conditions, the period of use exceeds five years.
Video about Nickel cadmium batteries
/ Nickel-cadmium batteries in power tools
Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries in power tools

Currently, the market share of hand-held construction tools is increasing every year with battery-powered tools. Battery packs power (battery) There are several types of power tools: nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal hydride and lithium-ion. Today, the most common batteries are nickel-based. This article will discuss in detail the characteristics.
nickel cadmium battery
The housing of nickel-cadmium battery cells (NiCd) is made of nickel-plated sheet steel, which is also the negative pole. The electrodes themselves are made in the form of foil from nickel-cadmium compounds according to agglomeration technology. Such foil is placed as a winding together with an insulating layer (separator), through which the electrolyte leaks. The electrolyte itself has a paste-like consistency and consists mainly of water and potassium hydroxide (potash lye). The battery cell is a closed system that is isolated from the external environment. Thanks to this, the electrolyte cannot leak out. At normal charging and discharge, gas exchange occurs inside the electrolyte. In case of abnormal operating conditions, such as short circuit or too high value charging current , in the battery cell as a result of the heat generation that occurs, overpressure . To prevent battery cell destruction, high quality battery cells
equipped with a safety valve that reduces pressure. In a charged static state, the battery cell voltage between the negative and positive poles is 1.2 V.
Maintenance: Nickel-cadmium batteries used in power tools are maintenance-free. They can be stored in either a charged or uncharged state. Once the battery is discharged, there is no need to charge it immediately. This is a significant difference between these batteries and lead-acid ones. and can damage the battery itself.

Volt-ampere characteristics:
The current-voltage characteristic of nickel-cadmium batteries depends on their size (capacity) and design. The more a battery cell is optimized to resist high current, the more stable the discharge voltage. If we compare batteries of the same design, but different capacities, then often a battery with a higher capacity has a greater resistance to high current.
As a result of numerous checks and tests, manufacturers of high-quality power tools have found the optimal balance between energy consumption and high current resistance.
Memory effect: When using nickel-cadmium batteries, they must always be completely discharged and only then recharged. In case of non-compliance of this rule a so-called memory effect may occur. Such partial discharges and subsequent partial charges can lead to the formation of crystals on the negative electrode, which reduces the initial capacity of the battery and drops the voltage during discharge. When connected electronic device
into the network, the voltage stabilization function is triggered as a result of premature shutdown of the device. Motorized appliances, such as power tools, respond by reducing their rotation speed. The memory effect, which is not too pronounced, is reversible. To do this, it is necessary to repeat several “normal” discharge-charge cycles, during which so-called fast chargers with a high charging current should be used.
Self-discharge: During storage, nickel-cadmium batteries discharge themselves. The self-discharge process mainly depends on the temperature and quality of the battery cell. Storage at high temperatures
and poorly manufactured battery cells contribute to self-discharge. At room temperature, the discharge time is approximately 3-4 months.
Temperature characteristics:
Like almost any chemical process, a chemical reaction occurs more slowly at low temperatures than at high temperatures. This primarily applies to thick electrolytes of nickel-cadmium batteries. Thus, at low temperatures they produce a lower discharge current than at room temperature. In addition, they cannot be charged with high current at low temperatures. The lower limit temperature is approximately -15C.
Nickel-cadmium batteries contain both nickel and cadmium compounds. Cadmium compounds are highly toxic. If not properly disposed of, cadmium from batteries can form highly toxic compounds that are potentially hazardous to the environment. Therefore, at the end of their useful life, nickel-cadmium batteries should be disposed of properly and recycled in accordance with applicable regulations. When properly disposed of, nickel-cadmium batteries have the highest recyclable percentage of any battery system. Thanks to recycling, nickel-cadmium batteries do not cause damage environment
. Therefore, manufacturers of high-quality power tools provide special recycling services for NiCd batteries. Despite the fact that nickel-cadmium batteries have been banned from production in the European Union since this year, these tireless workers are still used in many inexpensive and powerful standalone devices
ah (screwdrivers, electric shavers, flashlights).
Even if the operating instructions do not say anything about the type of battery of the device, it is quite simple to determine that it is a nickel-cadmium battery that serves as a current source - most often the charging time is indicated in the range of 5-12 hours and there is an indication of the need to independently turn off the charger after charging time. For nickel-cadmium batteries, fast pulse charging than slow DC . These batteries can give out more power
, which determines their choice for powerful standalone devices. Nickel-cadmium batteries are the only type of battery that can withstand complete discharge under heavy load without any consequences. Other types of batteries require incomplete discharge at relatively low power loads. Nickel-cadmium batteries do not like long-term charging under occasional light load. Periodic complete discharge is necessary for them as air is for a person - in the absence of complete discharge, large metal crystals form on the electrodes (which leads to the manifestation of the so-called “memory effect”) - the battery abruptly loses its capacity. For a long time and efficient work NiCd batteries require battery maintenance cycles - complete discharge followed by fully charged as a last resort once every 2-3 months.
Nickel-cadmium batteries are the most “foolproof” of modern mass-produced batteries - their use does not even require a system for monitoring battery parameters, which determines their use in inexpensive and powerful devices.
Charging with low currents for 5-12 hours allows you to do without any precautions in the form of charge-discharge control systems. When overcharged, the battery will simply slowly lose capacity (to the delight of the manufacturer). You must remember this when using “bad-boy” chargers (chargers without an automatic charge control mechanism). Therefore, it is best to charge a completely discharged battery and strictly observe the charging time, which will preserve the capacity NiCd battery for quite a long time.
When using “fast” charging (with a charge time of less than 5 hours), it is advisable to have a charger with a temperature sensor, since when charging the battery temperature rises, the capacity increases along with the temperature, and as the capacity increases, the charger can recharge the battery over required level, which leads to an even greater increase in temperature (the phenomenon of “thermal runaway” of the battery) and, at a minimum, to a deterioration in battery parameters. A similar situation exists when charging the battery at low temperatures. Temperature sensor allows you to shift the charge parameters depending on the battery temperature, as well as disconnect the battery from the charge when the rate of temperature rise exceeds 1 degree Celsius per minute or when the battery temperature reaches 60 degrees Celsius, which allows you to avoid the tragic consequences of thermal runaway.
To illustrate the need for a thermal sensor in a charger, I can give an example from two years ago of charging a nickel-cadmium battery for a professional screwdriver on a charger without a thermal sensor (in the photo - this is the charger itself), which allows you to charge the battery at an accelerated pace - in an hour. At that time, the temperature in the apartment was about 30°C, the charger should automatically charge the battery until the target voltage is reached and automatically turn off, which was stated in plain English in the instructions in the safety section. In the morning, the first battery from the set was charged without any incidents - after 50 minutes the charger turned off, in the evening the second battery presented a surprise while charging: due to the absence of a temperature sensor in the charger, the battery entered thermal overclocking mode. Since the charge was accelerated, the problem was noticed late - when the battery began to smoke and began to spray hot electrolyte. The charger, which was quickly disconnected from the network, was saved. The battery continued to suffocate in agony for a long time, trying to cause as much harm as possible when leaving for another world, but it failed and the damage was limited to the cost of the battery itself - 15USD. Since then, the charger has been connected to the network via a timer.
Despite their disadvantages, nickel-cadmium batteries still exist among us. I hope that a little theory and practical experience outlined in the article will allow the reader to get the maximum of what he is capable of from the nickel-cadmium battery of his device.