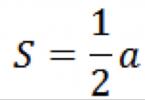It is carried out using one of two types of chargers, which can provide a constant current or a constant voltage during the process. Both methods are equivalent in terms of impact on the duration of the battery life. Before running down the battery, it is necessary to remove both terminals from it (plus) connected to onboard system car.
Constant Current Charging
To “calculate” the required amount of charging current to restore the battery, you need to divide the capacity of your battery, expressed in ampere-hours, by 10. For example, if the battery is 60 A / h, then the charging current on the device must be set to 6 A. The main disadvantage such devices - the need for hourly monitoring of the current strength and a fairly strong release of gases towards the end of the recovery process.
To reduce gas evolution, it is recommended to apply a stepwise decrease in current strength. When the voltage reaches 14.4 V, you need to reduce the current to 3 amperes (when charging a battery with a capacity of 60 A / h). If you have to charge the battery latest releases(they do not have holes for pouring distilled water), it is advisable to carry out another decrease in the value charging current up to 1.5 A (when the voltage rises to 15 V). We can assume that the battery is completely restored if the voltage remains unchanged for at least an hour (16.3-16.4 V).
Charging with a constant supply voltage
A heavily discharged battery has little resistance, so at the moment it is connected to the charger, the current can soar up to 40 A. To prevent this from happening and the device does not fail, maximum current limited to 20-25 A. The degree of battery charge and the duration of the recovery process are related to the voltage supplied to the battery:
- 14.4 V: battery charged by 70-80%;
- 15 V: 80-90%;
- 16.4 V: 100%, subject to the charging period (at least 20 hours, but not more than 24).
During charging, the voltage at the terminals approaches the value supplied by the device, respectively, the current drops and at the end of the process reaches zero. At this point, we can assume that the battery is fully charged. Usually, the end of charging is signaled by green indicator available on some devices. It should be borne in mind that the devices currently sold most often have a maximum output voltage of 14.4 V. Therefore, in order to be sure that the battery is fully restored, you need to leave it to charge for a day.
Any car battery you need to recharge - this is a kind of axiom! After starting the engine, the car's generator makes up for energy losses, but not always! For example, in " cold start”, when the temperature is overboard with extremely low rates of -20, - 30 degrees. The battery is cold and it cannot take energy normally, it needs to be warmed up, and if you move short distances, your battery will “undercharge”. As a result, a decrease in capacity may develop. In general, once a month (or maybe more often) you need to recharge the battery and it's clear that you need a charger for this! But how to choose it? After all, batteries come in different technologies? This article will detailed guide and video at the end. Definitely useful, so read - look ...
Of course, now batteries have stepped forward very much, if you do not take AGM, GEL and EFB technologies, then even conventional batteries are divided into three main subspecies - these are antimony, calcium and hybrid (described in detail these technologies in the article -). If “antimony”, this beast is quite rare on our shelves, because it is hopelessly outdated, then calcium and hybrid ones are very widely placed on our shelves. And for each battery you need the right charger, because let's say "calcium", many manufacturers recommend charging with currents of 16 - 16.5V,. And this is, as you know, completely different “chargers”!
Classic Charge
I already have an article about this, you can read it. But in short, then:
- The battery is RECOMMENDED to charge 10% of its capacity. For example, 60Ah, you need to charge 6 amps.
- You need to take into account the voltage of your battery, there are both 12 and 24 Volts
- The voltage must be set - so that the charge goes! EXPLAIN. For the 12 Volt version, you need to supply 13.2 - 14V (this is how much the generator gives), if the charge goes from 12.7 - 12.8V, then the battery will not be charged, or it will be very slow
- Gentle charge mode. Personally, I always RECOMMEND everyone to charge in the so-called "sparing mode", this is about 3 - 4% of the capacity. That is, if 60Ah, we set approximately 2 - 3A and charge until the charging current drops to 0.5A

This manual is suitable for most types of batteries, but not all. Therefore, if you choose a charger that has a maximum voltage of 14.5V, then modern options it can't ask.
Pulse or transformer
Now there are only two types of "chargers":
- transformer
- Pulse
Transformer models are outdated models that are based (as the name implies) on "transformers". They are bulky, heavy and are now practically not produced. The advantages of these models can be called reliability and fault tolerance.

Pulse models are much lighter and more compact, and most importantly they are cheaper, they just flooded the market now. With the development of technology, they have also become quite stable and fault-tolerant.
Look at your battery
Accordingly, we proceed from our tasks, that is, if you use old batteries, maybe also antimony ones, then almost every charger is suitable for them. But if you have "calcium" or even more so "charger" should be completely different, more perfect.

For example, the “antimony” option - if a voltage of more than 14.2V is applied to it, it will boil, and very intensively.
Also, calcium batteries are charged with a current above 16V, not every device can give it out.
A big plus is the desulfation system, with its help you can restore the battery (if it is still possible).
I want to note that the more perfect the charger, the more options it will be able to charge or even restore.
Charger and start-charger
When choosing, it is worth noting that there have been two types of units on the market for quite a long time:
- Conventional charging systems - they simply charge batteries.
- Start-charging systems - they not only replenish the charge, but can also start a car with a completely “dead” battery.

Many may think that a regular "charger" can also start a car - BUT IT'S NOT! They do not have high starting currents, and they can simply burn out. After all, when a car starts, it briefly consumes hundreds of amperes, for example, the average value for a passenger car is about - 300 amperes, and in winter period perhaps even more. It is this current that can give starter-charger.
Automatic, not automatic
For me personally, a high-quality charger is one in which I can control “from and to” with “hands”. For example, voltage, current, charge time, etc. However, there are a lot of so-called "automatic devices" (automatic chargers) on the market now. Usually Chinese made, of dubious quality. Actually, there are no designations on them, no voltage, no amperage - just connect it and it should automatically charge your battery! Should, but not required! Also, how does he know what type of battery is connected to it? YES, corny, you won’t even be able to control what voltage is on the terminals now!
Of course, such options are a great help for beginners who do not understand anything about such systems at all! It turns out, like a cell phone, connected the terminals and forgot, there is a bit of rationality in this. However, if you take such systems, then take serious firms, at least such as BOSCH.

As I wrote above, I personally am for a controlled option. I like to set currents and voltages myself, set algorithms (by the way, all serious “chargers” are now programmed). For example, for calcium batteries, the so-called “swing” is needed - if you exaggerate, when the current is one for several minutes, with one voltage, but the next few minutes are different, with a different voltage. Cheap "machines" by default are not capable of this.
Therefore, if you are planning to take a “charge”, then I personally advise you to take it with the possibility of manual adjustment, and now they have excellent instructions that even a “teapot” will understand.
Desulfation mode
It's real useful mode. from hot weather or deep discharges sulfates of sulfuric acid can form on the plates, while the density of the electrolyte will drop. These sulfates seal the plates and the capacity of the battery drops significantly. Sometimes the capacity loss can be 70 - 80%! With such indicators, it is impossible to start the car engine.

Removing these sulfates is quite difficult,. However, there are devices that do this in normal mode, with charge-discharge cycles. Just put in your battery and it will last for hours, probably days. Sulfates are broken, the surface of the plates becomes clean, the capacity is restored. It should be noted a very useful mode.
Battery health check
Many batteries are maintenance-free, so to speak, they cannot be opened (without surgical intervention) and it is really impossible to understand when one of the cans has failed. Sometimes it is corny jumped. If in a serviced battery you unscrew one plug and a dark electrolyte is visible, then in an unattended battery, this cannot be done. Although the voltage will drop to 10 - 10.5V. So modern chargers can detect a closed jar and state a "verdict", just useful feature.
Measurement and control of battery capacity
Again, not all chargers, but only the most advanced ones, can show battery capacity. And both the residual and the one they take. A very useful feature. That is, you can clearly see how much your battery has taken, how many Amperes in what time.

As a result
So, let's go over the main steps when choosing a car charger:
- 12 or 24 volts. Often if you passenger car, enough for a 12 volt system.
- An automaton is not an automaton. Personally, I advise a manually tuned unit, preferably with programs
- Charger or start-charger. If you have your own garage, then a starter-charger will not be superfluous. It will start the engine of your car, even if there is no battery at all. However, such a unit costs almost twice as much.
- Ability to charge AGM, GEL and calcium batteries. On many modern "chargers" such information will be indicated. THIS IS A USEFUL FEATURE. Because batteries are developing now. Often this means applying voltage from 15 to 16.5 volts
- The presence of a desulfation mode
- Health check
- Capacity check
- Programmable charge. It will be useful if you can program the charge cycle, that is, one current and voltage is supplied now, another in a few minutes, etc.
Actually, these are all functions, I did not specifically point out the manufacturers because there are really a lot of them, even on our Russian market There are very good devices, such as "ORION VIMPEL"(they are very flexibly programmed). Also, many people ask me if it is possible to charge IMAXB6 car batteries? Of course you can, this device is generally universal. The main thing is to choose the right power supply and set the right program.
Now let's watch a short video.
I end here, I think it was useful, read our AUTOBLOG, subscribe to updates.
As power sources modern cars lead-acid batteries are used. The choice in their favor by automakers was not made by chance - such batteries are less amenable to discharge in cold conditions than others and are able to restore performance even after intense loads associated with starting a cold engine. Car batteries are also called starter batteries - precisely because it is due to the use of their energy that the car engine “comes to life”.
The urban driving cycle, when the engine runs for a long time at low and medium speeds, does not allow the generator to fully supply the car with electricity and charge the battery.
When the motor is running, power electrical network The car is carried out mainly due to the generator, which simultaneously charges the battery, restoring the charge. But the urban driving cycle, when the engine runs for a long time at low and medium speeds, does not allow the generator to fully supply the car with electricity and charge the battery. In addition, modern cars, as a rule, are “stuffed” to the top with consumers of electricity.
These circumstances, combined with the natural loss of electrolyte density during operation, force the battery to be restored from time to time using external power sources - chargers. How to properly charge your car battery charger and will be discussed in this article.

Hydrometer for checking the density of the electrolyte
First of all, you need to check the electrolyte level in the battery. The battery plates must be completely immersed in liquid (or gel - in the case of). The density of the electrolyte under normal conditions should be 1.28 g/cm3. True, sometimes new batteries with a density of 1.24 - 1.25 g / cm3 are also on sale, but this does not mean that such batteries are defective - they are simply designed to work in tropical latitudes.

Battery electrolyte density table
The density measured by the hydrometer is, if necessary, corrected by topping up with distilled water or electrolyte, depending on the measurements. If it is lower than or equal to 1.1 g/cm3, then it can be restored by adding a corrective electrolyte with a density of 1.4 g/cm3.
The voltage of a healthy car battery must be at least 12 volts.
The voltage of a charged car battery must be at least 12 volts. It is measured by connecting a voltmeter (or multimeter in voltmeter mode) to the battery terminals. The most obvious way to show the state of the battery is a voltmeter with a load resistance, which, when connected, causes a current approximately equal to the current in the circuit of the included starter on the car. If the battery is good, then the voltage at the battery terminals is restored when the resistance is turned off.
Voltage measurements before and after the load should also be made when the battery is sold in the store, they will show whether the new battery and whether it needs to be recharged.

Battery voltage test
You can also use a voltmeter to check the battery charging from the generator by connecting a voltmeter to its terminals with the engine running. The voltage should be about 14 volts, with consumers turned off - headlights, glass heating, etc. Along the way, you can find out if the battery is charging at idling- if the voltage at the terminals is less than 14 volts, then it is necessary to check the condition of the generator and the service belt.

Table of battery voltages when discharging
In addition to checking the actual condition of the battery, check the possibility of current leakage through the battery case - dirt and moisture lead to loss of charge. You can simply, for prevention, clean the battery case from dirt, especially at the terminals, and wipe it with a solution of baking soda - it will “extinguish” the electrolyte if it gets on the case. You can also use soap instead of baking soda.
Current leakage through the case is easy to check with an LED with extended leads. It is enough to connect one output of the LED to the battery terminal, and “scan” the surface of the case with the other, touching it in different places.
Rules for charging a car battery
General process requirements:
- Unscrew the plugs from the battery case - otherwise, when gases are released, it may be damaged.
- Observe the polarity when connecting the charger.
- Keep sparks away from the charging area - the liberated hydrogen and oxygen combine to form nothing but explosive gas. A battery explosion is possible from sparks caused by the operation of a grinder, a welding machine, careless smoking, etc.
Before charging the battery, be sure to unscrew the plugs from the battery case.
Answers to the most common questions related to battery charging

The charging current should not exceed 10% of the battery capacity
IN:- "Can I charge the battery at home?"
ABOUT:- It is possible to charge the car battery at home, but with precautions related to the release of combustible gases and the possible contact of electrolyte with household items.
IN:- "Do I need to unscrew the plugs when charging the battery?"
ABOUT:- It is imperative that the pressure of the released gases does not damage the battery case.
IN:- "What current to charge the battery?"
ABOUT:- The current strength is set to 10% of the capacity. That is, to charge a battery with a capacity of 60 a / h, the value of the charging current must be 6 amperes.
IN:- "Should the battery boil when charging?"
If any “bank” of the battery boils immediately after the start of charging, then this indicates a malfunction.
ABOUT:- This is a normal phenomenon associated with chemical oxidation-reduction reactions. In fact, the evolution of gases cannot be called boiling - it is not associated with the heating of the electrolyte. But if any "bank" of the battery boils immediately, then this indicates its malfunction and the battery can only be disposed of. Rapid boiling after a long period of time is an indirect sign that the battery is charged.
IN:- "How long does it take to charge a car battery with a charger?"
ABOUT:— It depends on the degree of discharge of the battery. Be prepared that the process will take 8-10 hours. The charging current also affects the charging time - the higher it is, the less time it will take. The most high-quality battery charging low current. It is desirable to perform several charge-discharge cycles - as proven in practice, this method is most effective. You can discharge the battery using a 12-volt car lamp 21 - 55 W. Correctly charge a completely discharged battery with a current equal to 1/20 of the battery capacity - i.e. to charge the "90th" battery, set a charging current of about 4 - 5 amperes.
IN:- How to charge maintenance-free battery car?"
ABOUT:- Maintenance-free (gel) batteries are sensitive to excess charging voltage, so you need to use an accurate charger that allows you to adjust the voltage, not allowing the latter to be higher than 14.4 volts - otherwise the gel will “melt” and its volume will need to be restored.
IN:- "Is it possible to charge the battery in the cold or immediately from the cold?"
ABOUT:- It depends on the density of the electrolyte and on the readings of the outdoor thermometer. The electrolyte with a density of 1.28 g/cm3 does not freeze up to minus 40 degrees. If the battery is defrosted, then charging it will be a waste of time - the warped plates are most likely closed, and their active filler will fall to the bottom. Such a battery can only be disposed of, but if the battery is not defrosted, then it will be successfully charged even in the cold.
IN:- "Is it possible to charge the battery without removing the terminals?"
The battery can be charged without removing the terminals, but the ignition must be turned off.
ABOUT:- You can, if you want to charge the battery without removing it from the car. To reduce charging time, try not to use power consumers during charging. onboard network and do not exceed charging voltages above 14 volts.
IN:- "Can I charge a charged battery?"
ABOUT:- Absolutely nothing - there will be a loss of electrolyte due to boiling.
IN:- "How many volts should a charged battery show?"
ABOUT:— The standard battery has a rating of 12 volts. A freshly charged battery may have a slightly higher value.

Car battery chargers
The battery can be charged without a charger - by "lighting" it from another battery, but in this way it will not be possible to fully restore its charge. Therefore, it is advisable to acquire a device - buy it or make it yourself.
The battery can also be charged without a charger by connecting it to another battery, but full charge will not.
Commercially available chargers are fully capable of converting normal 220V mains current into a current capable of restoring battery charge. As a rule, they are equipped with an ammeter to control the current strength and a switch with which it is regulated. In addition, there are start-up chargers on sale that allow you to immediately start the engine, even if the battery is completely discharged.
But motorists often make "charges" for car batteries with their own hands. Despite the seeming primitive homemade devices, they successfully cope with their duties - subject to a careful selection of elements for assembling the circuit and setting the device “for their own” battery.

Various schemes of car battery chargers
You can see one of the simplest battery charging schemes in Fig. 1 - the most simplified option, but you can use not to lower the voltage load resistance(indicated as a lamp in the figure), and use a step-down transformer 220/12 V, use as a rectifier diode bridge car generator.
In addition, you can improve the circuit by installing several resistors and switches that allow you to adjust the current by jumping the resistance. Moreover, the scheme can be constantly improved in other ways - you can learn about them yourself if you show interest.
A modern car is equipped with sophisticated electronic devices, powered from the on-board electrical network of the car with a voltage, as a rule, 12 volts. These devices are powered by a car battery "rechargeable battery, battery", which, when the engine is running, is charged from electric generator. The engine can only be started by an electric starter driven by the energy stored in the battery.
When the engine is idle for a long time, the battery is discharged from working devices or as a result of self-discharge, and starting the engine becomes impossible. The way out is to start the engine from the starting device or charge the battery from the charger. Of no small importance for this is knowing how to properly charge the car battery with a charger.
The battery generates electrical energy as a result of a chemical reaction that occurs between the battery plates placed in the electrolyte.
Batteries are maintenance-free and serviced. During the chemical reactions associated with the charge and discharge of the battery, water evaporates from the electrolyte, so it is necessary to periodically check the electrolyte level, and top up with distilled water when the level drops.
AGM batteries "batteries with absorbent glass mats" and gel batteries are maintenance-free. On cars, depending on their purpose, the following types of batteries can be installed, the characteristics of which are summarized in the table

Before charging the battery, you should select the charger "ZU", which is supposed to be used in the future.
- Pre-launch memory. The simplest ones allow you to charge the battery to restore its electrical capacity. You can charge the battery both in a separate room and without removing it from the car "having first disconnected the battery from the car's on-board electrical network."
- Charging and starting devices "ZPU". They provide a very large output current, sufficient to operate the starter and start the engine. It also allows you to charge the battery.
What you need to know about battery charging
During regular trips by car, the battery is regularly recharged and is in a state of constant readiness. But during long downtimes of the car, the battery must be charged monthly until the capacity is fully restored. The battery has the following passport characteristics that determine the battery charging mode:
- Rated voltage - for passenger car usually 12 V;
- Electrical capacity - usually selected based on the operating capacity of the engine within 55-200 ampere-hours "Ah".
The voltage of the charger is selected according to the nominal voltage of the battery, and must be slightly higher than it to provide the required charging current.
The time to fully charge a discharged battery is determined by its electrical capacity and charge current. The higher the current, the faster the battery is charged, but at the same time its wear increases, and you should resort to the accelerated charge mode only when absolutely necessary.
The normal charging current of a battery is 10% of its nominal capacity. As an example, with a battery capacity of 66 Ah, the normal charge current is 0.1 x 66 = 6.6 A.
Preparing the battery for charging
Before charging the battery, you should carefully study the instructions for the used charger, which, in addition to describing the principle of operation and the device of the charger, contains information on how to properly charge the car battery.
First of all, inspect the battery, check the electrolyte level in it, the integrity of the case.
The degree of battery discharge can be estimated by measuring its voltage under load with a load plug. The voltage at the terminals of a fully discharged lead acid battery with a nominal voltage of 12 V, it usually does not exceed 7.8 V. With a 50% discharged battery, the voltage drops to 9 V.
Some batteries are equipped with a color discharge indicator mounted on the case cover. A diagram explaining how to use the indicator is usually pasted near the indicator.
In case of lack of electrolyte, add up to required level distilled water. The battery cover has a vent hole for fumes to escape during battery operation or charging. Make sure the vent is not clogged.

Do not charge the battery in a residential area due to evaporation during electrolyte charging. You can charge the battery without removing it from the car, or in a non-residential area.
First of all, it is necessary to connect the battery to the charger correctly, observing the polarity. At wrong connection, most likely, the fuses in the memory will blow.
There are two battery charging modes:
- with a constant charge voltage "in this case, the charging current changes";
- with the constancy of the charging current "in this case, you have to change the charge voltage."
The method of charging with a constant voltage is the simplest. Increase the charger voltage with the regulator, starting from the minimum voltage, until the charging current is equal to 10% of the battery capacity. In the future, until the end of the charge, the voltage of the charger is not regulated and remains unchanged. As the battery charges, its voltage rises and the charging current decreases.
With a complete decrease in the charge current, the battery is considered charged "however, it is not fully charged in this mode." Such charging takes 10-13 hours.
Constant current charging refers to charging in 3 stages, with the charging current changing at each stage. First, the charge current is set to 10% of the battery capacity "6.6 A in the example."
When charging, you should monitor the battery voltage in the charge mode “this voltage is shown by the charger voltmeter”.
As the charge increases, the voltage will increase, and when the value of 14 V is reached, the charging current should be reduced by 2 times “up to 3.3 A in the example” in order to avoid boiling of the electrolyte. When the voltage increases to 15 V, the current should be lowered by another 2 times "up to 1.6-1.7 A in the example." In this mode, the battery is charged until it is fully charged, which is determined by the invariance of the voltage for an hour.
You can check if the battery is charged by disconnecting it from the charger and checking its performance with a load plug. The voltage of a fully charged battery under load is 10.2 V "not lower".
Also, an indicator of the health of a charged battery is the ability to operate a starter from it, followed by starting the car engine.

Even motorists with basic knowledge of electrical engineering are often faced with the task of how to properly charge a car battery. First of all, you should decide whether you need a start-charger or a simple charger is enough. After purchasing the charger, you should decide on the preferred method of charging the battery.
You can choose from a forced charge mode with a high current, which should be resorted to only in case of emergency, an accelerated charge, or one of two more gentle charge modes - with a constant charging voltage or a three-stage one with a constant charging current at each stage and the need to regulate the charge voltage three times .
Armed with the knowledge of how to properly charge your car battery, you'll prolong its life and be sure it's ready to go.
While the power plant of the car is idle, the on-board network is powered from external source power supply - car battery. Also, by means of the electric power of the battery, the start of the power plant is also carried out.
Any motorist should know how and how to charge the battery of his car
The need to properly charge the car battery
But the battery does not generate energy to power the network, it only stores it in itself, gives it away if necessary, and then restores its charge from.
The charge-discharge cycle does not benefit the battery itself, over time its charge decreases, that is, the battery is slowly discharged, it is not possible to completely restore the amount of energy from the generator, in the end the battery charge will no longer be enough to start the motor. In this case, the question arises sharply: how to charge the car battery. This operation is performed by chargers. But before describing the process of charging a battery, let's figure out what kind of batteries are on cars, their main parameters that are taken into account when recharging, types of chargers, the principle of their operation, the rules for charging a car battery and what should not be done when performing an operation.
Video: Battery explosion
All batteries are structurally similar. There is a set of plates that play the role of electrodes, some are positive, others are negative. In order for a chemical reaction to occur between the plates, as a result of which electricity is released, the space between the plates is filled with electrolyte. Depending on the type of battery, either an acid solution with water or an alkali solution with water acts as an electrolyte.
Types of batteries
The following types of batteries are used on cars: acid, alkaline and gel. There is another type of battery - lithium-ion, but due to its characteristics, these batteries cannot start the engine, so they are used in cars so far only as additional element nutrition.

This is how a car battery works
At acid batteries electrodes are made of lead, which contains additional impurities. Lead as an electrode material is used because this material has a good energy capacity and can deliver large currents in a short period of time. The electrolyte in these batteries is an acid solution. These are the most common batteries that are used in a car.
Alkaline batteries have nickel-cadmium or nickel-iron plates instead of lead. And the space between them is filled with a solution of caustic potassium. These batteries are passenger cars are not often used, since their current strength is lower than that of acidic ones.
Appeared relatively recently. In fact, this is the same acid battery, only its electrolyte is brought into a jelly-like state. These batteries are promising, but a number technological features These batteries do not allow them to be widely used, and they are not solid.
In addition, batteries are also divided into serviced and unattended. Acid batteries are only served. And all because during a chemical reaction, part of the water from the solution evaporates. In order for the electrolyte to have the appropriate density, it is periodically necessary to check the state of the electrolyte and, if necessary, add water.
Water for topping up the battery is used only distilled.
Maintenance free are gel batteries. They have hermetic case. During a chemical reaction, water does not evaporate from them. Therefore, topping up is not required.
Types of chargers for charging the battery
In the future, we will consider the correct charging of the battery using the example of common acid batteries. But for now let's go through the chargers.

Battery charger
Any charger is a power converter. The most simple circuit charger (charger) is a step-down transformer and a diode bridge. The principle of operation is as follows: the alternating voltage of the network 220 V, passing through the transformer and the diode bridge, is converted into a constant voltage of 14-15 V, which is required to charge the battery.
Often, additional control sensors are included in the design of the charger - ammeters and voltmeters, voltage and current regulators, fuses. Although there are also chargers in which the current and voltage for each battery are selected automatically.
Something else useful for you:
Features of car battery charging
Before you charge your car battery, there are a few things to consider for charging your car battery.
- The most optimal current for charging the battery is 10% of the nominal energy capacity of the battery. That is, with a battery energy capacity of 60 Ah, the current strength should not exceed 6 A.
- The optimal voltage at the charger terminals is + 10% of the nominal voltage of a fully charged battery. For example, a fully charged battery has a terminal voltage of 12.6 V. 10% of the nominal voltage is 1.26 V, add it to 12.6 V and get the optimal voltage of 13.86 V.
- Spend fast charging batteries is possible. Such charging is carried out with currents of large values \u200b\u200b- 20-30 A. But such charging damages the battery, so it is better to refrain from such charging.
- When charging gel battery it is important not to exceed the critical voltage for such a battery, which is usually 14.2 V.
These are the main criteria that are taken into account in order to properly charge a car battery. Let's proceed directly to how to charge the car battery.
Preparatory work
First you need to make sure that the battery is really discharged. To do this, it must be removed from a niche in the car. In addition to the natural discharge of the battery due to its operation, the cause of the discharge may be damage to the battery case, as a result of which the electrolyte has leaked out and the chemical reaction does not take place in it. Therefore, after removing it, it must be cleaned of dust, dirt, and the battery case should be carefully inspected. If there is a crack and electrolyte leaked out through it, such a battery can no longer be used.
To determine whether the battery is discharged, you can use the color indicator, which is often installed on the housing cover. The colors in the indicator can be different, so you should pay attention to the sticker with an explanation, which is usually pasted next to the indicator.
You can also check the state of charge of the battery by the voltage at the terminals. To do this, you can use the usual tester. With a discharged battery, the voltage will be lower than the nominal voltage.
Before you charge the car battery, you should also check the electrolyte. Through the filler plugs, you can monitor the state and amount of electrolyte, in normal condition the electrolyte must be clean, transparent and free of impurities, and its level must be above the plates. At a lower level, you need to add distillate.
You should also check the vent hole in the battery cover. It must not be clogged, otherwise the fumes will not come out.
How to charge a car battery? Charging process
Then you can directly charge the battery. An important point is the evaporation of the electrolyte during recharging, so you should not do this in a residential building. Also, first connect the charger to the battery, and only then to the network. You need to carefully consider the correct connection of the charger to the battery, otherwise, if connected incorrectly, the fuses of the charger will fail.
Video: How to charge a car battery
The process of charging the battery with a charger is carried out in two ways.:
- in the first method, charging is performed at a constant voltage value, usually this value is 14-16 V. And the current strength is a variable value. At the beginning of charging, the current strength is large, it can reach 25-30 A, but as the charging progresses, the current strength decreases.
- in the second method, the current strength is constant, and the voltage varies. This method more complex, and one must fully know how to properly charge a car battery with such a charge.
Charge a car battery with a charger that uses the constant voltage- not difficult. It is enough to set the current strength with the regulator at the level of 10% of the energy intensity of the batteries. As you recharge, the current will drop. A signal that the battery has fully restored its charge will be lowering the ammeter needle to “0”. Usually, it takes 10-13 hours to fully recharge with such a current strength.
Recharging the device direct current more difficult, and you need to know how to recharge a car battery with such a charger. Since this device the current strength parameter is set, then at the beginning of charging, the current strength is set in the amount of 10% of the energy intensity. With such a current, the battery is charged to a voltage of 14 V, after which the current should be reduced by half and charged with such a current to a voltage of 15 V, after which the current should be halved. The signal of a full charge of the battery will be the retention of the voltage indicator at the same level in the indicator for an hour.

Battery voltage test
After charging, if possible, check the voltage at the battery terminals by applying load fork. If it is not there, you can make sure that the battery is fully charged by installing it on the car. A charged battery should "briskly" turn the starter and start power plant. In principle, that's all you need and it's important to know to charge your car's battery.