The vacuum booster is one of the integral elements brake system car. Its main purpose is to increase the force transmitted from the pedal to the master cylinder. Due to this, driving becomes easier and more comfortable, and braking is more effective. In the article we will analyze how an amplifier works, find out what elements it consists of, and also find out whether it is possible to do without it.
Vacuum booster in section
The main functions of a vacuum cleaner (a common designation for a device) are:
- increase in the force with which the driver presses the brake pedal
- providing more efficient work braking system during emergency braking
The vacuum booster creates additional force due to the resulting vacuum. And it is precisely this increase in the event of emergency braking of a car moving with high speed, allows the entire brake system to work with high efficiency.
Vacuum brake booster device
Structurally, the vacuum amplifier is sealed housing rounded shape. It is installed in front brake pedal V engine compartment. The main brake cylinder is located on its body. There is another type of device - a hydraulic vacuum brake booster, which is included in the hydraulic part of the drive.
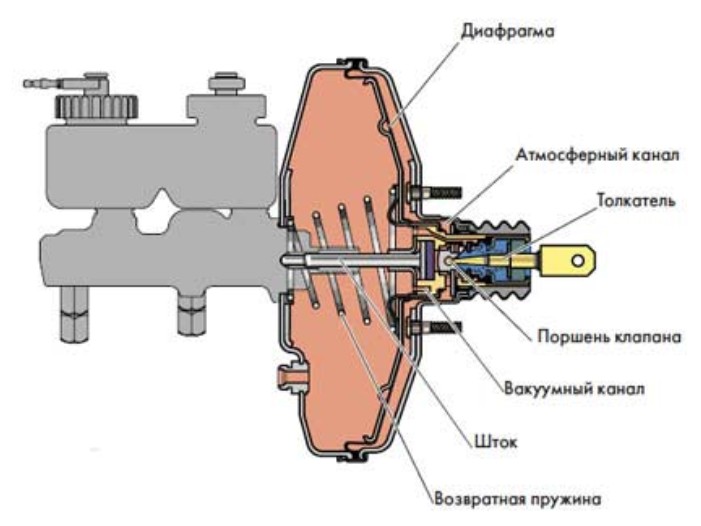 Scheme vacuum booster brakes
Scheme vacuum booster brakes The vacuum brake booster consists of the following elements:
- frame
- aperture (for two cameras)
- follow-up valve
- brake pedal pusher
- brake hydraulic cylinder piston rod
- return spring
The body of the device is divided by a diaphragm into two chambers: vacuum and atmospheric. The first is located on the side of the main brake cylinder, the second on the brake pedal side. Through the check valve of the amplifier, the vacuum chamber is connected to a source of vacuum (vacuum), which on cars with a gasoline engine is used by the intake manifold before supplying fuel to the cylinders.
 Vacuum pump
Vacuum pump In a diesel engine, the source of vacuum is an electric vacuum pump. Here the vacuum in the intake manifold is insignificant, so the pump is a mandatory element. The check valve of the vacuum brake booster disconnects it from the source of vacuum when the engine is stopped, as well as in cases in which the electric vacuum pump fails.
The diaphragm is connected to the piston rod of the main brake cylinder from the vacuum chamber side. Its movement ensures the movement of the piston and injection brake fluid to the wheel cylinders.
The atmospheric chamber in the initial position is connected to the vacuum chamber, and when the brake pedal is pressed, it is connected to the atmosphere. Communication with the atmosphere is provided by a follower valve, the movement of which occurs using a pusher.
In order to increase the braking efficiency in an emergency, the vacuum brake design can include an emergency braking system in the form of an additional electromagnetic rod drive.
Operating principle of a vacuum brake booster
The vacuum brake booster operates due to different pressure in the cells. In this case, in the initial position, the pressure in both chambers will be the same and equal to the pressure created by the vacuum source.
When you press the brake pedal, the pusher transmits force to the follower valve, which closes the channel connecting both chambers. Further movement The valve facilitates the connection of the atmospheric chamber through a connecting channel with the atmosphere. As a result, the vacuum in the chamber decreases. The pressure difference in the chambers moves the piston rod of the master cylinder. When the braking ends, the chambers are reconnected and the pressure in them is equalized. The diaphragm, under the action of the return spring, takes its initial position. The vacuum cleaner works proportionally to the force of pressing the brake pedal, i.e. The harder the driver presses the brake pedal, the more efficiently the device will work.
Vacuum booster sensors
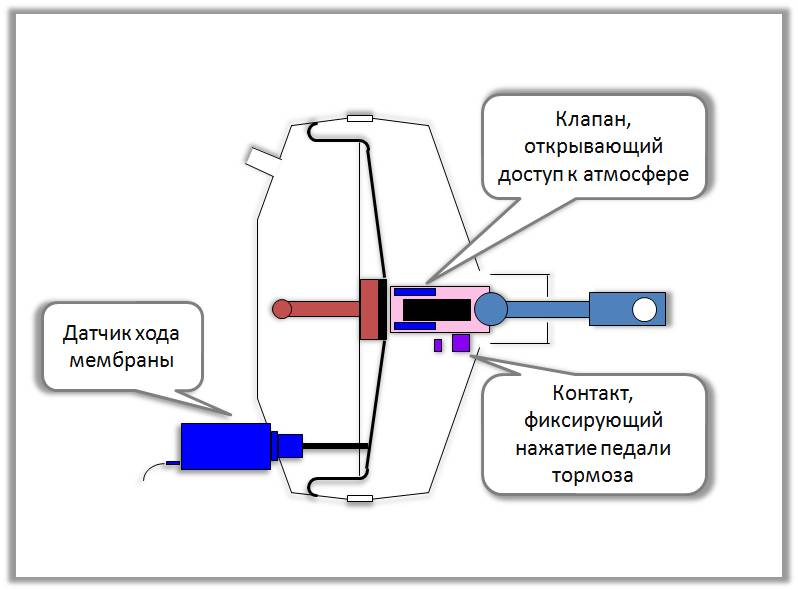 Vacuum booster with diaphragm stroke sensor
Vacuum booster with diaphragm stroke sensor Efficient operation of the vacuum booster with the highest coefficient useful action provides pneumatic system emergency braking. The latter includes a sensor that measures the speed of movement of the amplifier rod. It is located directly in the amplifier.
There is also a sensor in the vacuum chamber that determines the degree of vacuum. It is designed to signal a lack of vacuum in the amplifier.
Conclusion
The vacuum brake booster is an indispensable element of the braking system. Of course, you can do without it, but it’s not necessary. Firstly, you will have to spend more effort when braking, you may even have to press the brake pedal with both feet. And secondly, driving without a booster is unsafe. In the event of emergency braking, there may simply not be enough braking distance.
The vacuum brake booster of the fourteenth is a casing with a valve inside. It is divided into two parts by a rubber layer - a diaphragm - one part is atmospheric, and the second represents the vacuum space, which is connected to the intake pipe from the engine.
The amplifier valve is a plastic casing that contains the main parts that are subject to wear and cause trouble for the driver in the form of gearbox rattling. The composition is as follows: on the support bushing there is a rod, which is adjacent to the piston and its own buffer. Actually, the valve itself is on its pusher and return springs along with the filter.
The vacuum booster functions as follows: you press the brake to the floor, at this time the piston and valve pusher move in such a way that this opens the space between the two compartments of the unit. Then, a vacuum compartment moves into this space and takes in air. The air presses on the damper between the two parts of the amplifier, creating different levels pressure in one and the second part. Due to this difference, the valve itself and the rod move, respectively. By lowering the pedal, all parts return to their places, the system ceases to function.
As with all parts of the system of any car, repairs to the vacuum brake booster are inevitable. In order to decide on repair work– whether this is a DIY garage repair or should you go to a service center – you must first determine the signs of a malfunction in the vacuum brake booster of the VAZ 2114.
Checking the amplifier assembly
The answer to the question of how to check the vacuum brake booster is suitable not only for the fourteenth VAZ model, but can also be applied to the thirteenth and fifteenth.
The process is like this:
- Press the brake to the floor 4-5 times with the engine not running. This will create uniform pressure in the two parts of the amplifier. When you press the brake, the valve will immediately show itself: if it squeaks, then you need to seriously think about it.
- After the pressure has become uniform, start the fourteenth. But at the same time you need to keep the brake to the floor. If everything is in order with the brake booster system, the pedal will rise after the engine starts. If this does not happen, then repair is definitely required.
- In the event that you realize that there is a problem with the amplifier, you need to look to be sure how the hose is secured and what condition the flange is in. If the fastenings at any point do not correspond to the norm, this may affect the fact that the pedal does not lift, and in fact the fault will be on a separate incorrect fastening, and not on the entire system as a whole.
Reasons for replacing the brake booster
Brakes are a whole system. Therefore, as soon as you have checked the amplifier, do not be lazy and check whether the brake fluid is leaking and whether the pedal itself is in order. Maybe it's worth looking at the brake master cylinder and generally running diagnostics. And if, nevertheless, you have not found any problems in the brake system, then you can think about how to change the vacuum on a VAZ 2114.
It is important to understand that replacing the vacuum on a VAZ 2114 or any other VAZ model is a mandatory process. If the unit is malfunctioning, then the engine is also malfunctioning. The power that the engine will produce depends on the correct functionality of the amplifier. What Russian doesn't like drive fast? As they say, if you love to ride, you also love to change the vacuum.
How to replace?
For this process you will need the following tools:
- Simple screwdriver
- Pliers
- Spanners 13, 17
- Specific wrench for unscrewing brake pipes
- It’s worth buying new fittings and plugs
The question of how to change the vacuum booster on a VAZ 2114 is a very common one. If the perception of the text is not accurate enough for you, you can always rely on our article.
Step by step process:
- The brake cylinder will interfere with removing the booster. Therefore, you can first remove it, or simply disconnect the tube fittings from it and move it to the side. It's whatever your heart desires.
- But the cylinder is not the main obstacle. Unscrewing the amplifier fasteners is, in principle, not an easy task, or rather inconvenient. We start with the valve: remove the hose mount, pull out the support sleeve and pull out the brake pin.
- Then we take the key to 13 and begin to unscrew the 4 fastenings of the amplifier.
- Having endured troubles and inconveniences, we are preparing to install a new one in its original place. But first, you need to install a special mounting frame on the purchased amp. We wake it up with a key set to 17 and only then put it inside the car.
- The assembly sequence is simple, but important point from the point of view of convenience, the primary action is to connect the brake (pedal) and the booster (all this with just a finger). And then attach the entire unit to the fourteenth.
Unit cost
It is better to find out how much a vacuum brake booster for a VAZ 2114 costs directly from stores. Since the regions are different, price categories different and easier to navigate the terrain, locally. approximate cost ranges from 2,000 to 3,000 rubles. Installing it in the service will cost a third, or even half, of the cost. Despite the inaccessibility of the unit and some inconvenience, it is much easier to change the amplifier yourself. The frequency of breakdowns or replacements directly depends on the quality of the track, driving style and the general wear and tear of car parts, in particular the chassis. Therefore, it is difficult to say that there is any specific regulatory period. The only thing you need to remember is about timely diagnosis: sometimes it’s worth getting confused and going over your fourteenth with the eye of a caring owner. And, of course, you shouldn’t delay repairing or replacing the unit.
If you notice that you have to apply significant force to slow down or stop the car, and the brake pedal travel when the engine is running has decreased and become stiffer, you need to diagnose the vacuum brake booster (VBS). if necessary, it can be easily done by hand.
Before checking the vacuum brake booster, you must make sure that the hose connecting its valve to the intake manifold is tight. This can be done using visual inspection its integrity or an attempt to pump air using a compressor with a pressure gauge into a hose or rubber bulb that has been removed and plugged on one side.
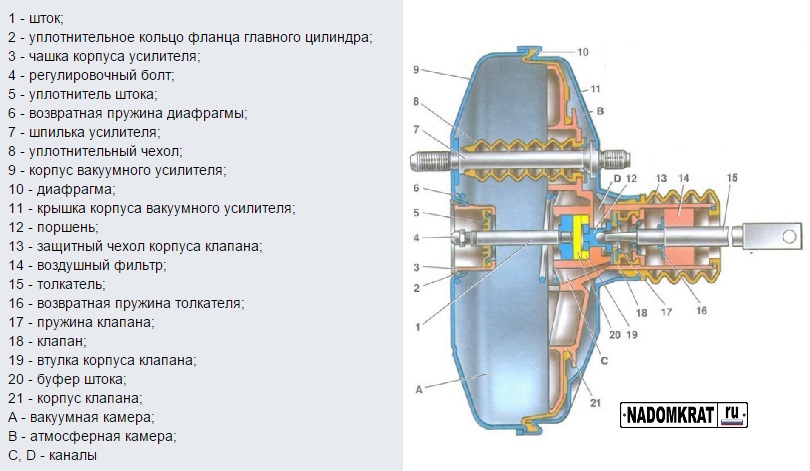
Vacuum brake booster device
The vacuum brake booster is designed to improve the usability of the braking system. A car without VUT would brake very hard - the force transmitted to the pedal in this case would be very significant, which would affect driving safety for the worse.
The VUT is usually located directly behind the engine shield. Structurally, this element is made in the form of a non-separable metal block connected to the main brake cylinder and brake fluid reservoir.
The vacuum sealer includes the following elements:
- Frame.
- Separating membrane (made from flexible material).
- Brake pedal pusher.
- Hydraulic cylinder rod.
- Return spring.
- Follow-up valve.
The principle of operation of the vacuum seal is based on the difference in atmospheric pressure, as a result of which a vacuum is created that ensures the formation of pressure (and at the same time the transmitted force) in the brake system.
Inside the VUT there is a diaphragm in the form of a partition. Each of the chambers (cavities) separated by a diaphragm is sealed. Moreover, the chambers are equal to each other in volume.
One of the chambers communicates freely with the atmosphere (it is called the atmospheric part), the second is connected to a hose leading from exhaust pipe engine. On this side, a lower pressure compared to atmospheric pressure is formed. This cavity is called vacuum; it is located on the GTZ side.
The atmospheric chamber, located closer to the brake pedal, contains a reverse valve. It is designed to prevent a decrease in pressure in the intake manifold of the engine. Due to this, fuel cannot enter the VUT mechanism.
The amount of vacuum in this cavity is controlled by a follow-up valve. The vacuum chamber, thanks to the reverse-acting valve, maintains the pressure at the same level. In other words, the membrane experiences the same pressure values from both chambers. The follower valve moves through a pusher, which is connected to the brake pedal. The purpose of the spring is to ensure that the diaphragm returns to its normal state after stopping braking.
In some situations, when the car is equipped with an emergency braking mechanism, the rod is equipped with a specialized electromagnetic drive.
As you can see, the design of the vacuum unit is not so complicated - in some cases, troubleshooting some VUT faults can be done on your own.
Checking the membrane and chamber tightness
There are several ways to check the serviceability of the vacuum brake booster (VBS), but to ensure that it is 100% operational, it is better to use them all. First of all, press the brake pedal several times with the engine off. When pressed for the first time, the pedal will lower with a fairly insignificant force by about 1/3 of the full speed, with each subsequent press it should become tighter and the stroke should decrease. If this does not happen, the VUT is most likely faulty, and diagnostics of the vacuum brake booster is required. Next, we will tell you how to check the vacuum brake booster on Kalina.
Thanks for subscribing!
If VUT diagnostics have shown ambiguous results and it is difficult to determine the difference in pedal stroke and pedal stiffness, you can try another method. Press the brake pedal two or three times and start the engine without removing your foot. There are several options for the development of events:
- If the pedal goes deeper a few centimeters, the vacuum brake booster is working properly. You can finally verify this by turning off the engine and not releasing the brake pedal for 30 seconds.
- If the pedal starts to rise, this indicates a leak in the vacuum chamber.
Checking the VUT check valve
Reason bad work The brake booster may be faulty check valve, to which the hose from intake manifold. To diagnose the latter, you need to remove the hose, remove the valve from the VUT body and put a rubber bulb from a syringe or hydrometer on it from the outside (to which the hose is connected) and squeeze it. If, after releasing the bulb, it remains compressed, the check valve is working properly.

Otherwise, it must be replaced. In a similar way, you can check the inlet hose for leaks in the absence of a compressor.
Diagnostics of the vacuum brake booster can be easily carried out in just a few minutes using simple manipulations without the use of any measuring instruments and tool. For a more objective check, try various ways, proposed in the article. Before doing this, do not forget to check the condition of the hose leading to the VUT from the intake manifold.
Today, rarely can anyone imagine the operation of the brake system without a vacuum brake booster. Next we will talk about malfunctions and repair methods for the unit in question. From a technological point of view, repairing a vacuum brake booster is not difficult, even if you decide to carry out the procedure yourself.
It is only recommended to take into account design features one or another car model, but the basic principle of the repair itself is similar for all models.
It is advisable to familiarize yourself with the structure of this unit before direct repair or replacement.
Vacuum brake booster device
Structurally, the vacuum brake booster is combined with the GTZ into one unit. For a person with developed intelligence, the scheme of action of the element in question will not present any difficulties. The body is divided into two parts, with the atmospheric part located on the side of the brake pedal, and the vacuum part on the side of the main brake cylinder.
Using a check valve, the vacuum chamber is connected to the intake manifold, which in turn is a source of vacuum. An electric vacuum pump is often used on diesel engines to ensure constant operation of the vacuum booster.
When the engine stops, the vacuum booster is disconnected from the manifold by the action of the check valve, which is why the vacuum brake booster is only able to operate when the engine is active. In the event of a malfunction or failure of the element in question, a similar disconnection occurs.
Due to the follower valve, the atmospheric chamber in its initial position is connected to the vacuum chamber and to the atmosphere when the brake pedal is activated. A pusher is connected to the brake pedal; due to it, the follower valve moves. A diaphragm is connected to the GTZ rod from the side of the vacuum chamber; it facilitates the pumping of brake fluid through the piston to the working cylinders.
Due to the return spring, the diaphragm moves to its original position at the end of braking. The amplifier design may also include electromagnetic drive stock Active brake booster is used in ESP system and its main purpose is to prevent rollover.
In general, the operation of a vacuum brake booster is based on the pressure difference in the atmospheric and vacuum chambers. It is due to this difference that the pusher is activated and promotes the movement of the GTZ piston rod.
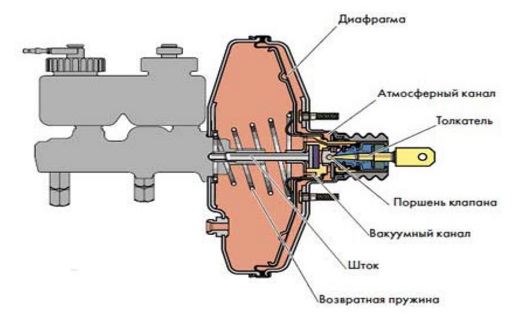
Malfunctions of the vacuum brake booster.
The first thing worth emphasizing is that malfunctions of the unit in question cannot contribute to the complete deactivation of the brake system. As a result, driving the car becomes more difficult and the driver is forced to put more effort into pressing the brake pedal. Traditional faults include the following:
- There is a malfunction inside the vacuum booster itself, for example, aging valve rubber or diaphragm rupture. IN in this case the valve will begin to leak air.
- A break or depressurization of the hose connecting the engine manifold to the vacuum brake booster. In this case, you will be able to hear the hissing of the element in question. Be sure to check the tightness of the clamps and the hose itself for breaks or cracks.
How to check the vacuum brake booster?
- If the engine starts to stall, diagnose the serviceability of the vacuum booster. Depressurization is often accompanied by air suction into the intake manifold pipe; therefore, the air-fuel system that enters the engine cylinder becomes sharply leaner.
- As a second diagnostic option, make about five strokes using the brake pedal at engine not running. Then, in the middle of the stroke, lock the pedal and start the engine. If the pedal falls during startup, the vacuum booster is functioning. If it remains motionless, then it is necessary to replace or repair the vacuum brake booster.
- At visual inspection It is strongly recommended to pay attention to the presence of smudges that may appear on the body of the vacuum booster.
- The vacuum brake booster must be adjusted periodically.
For repair or replacement, it is necessary to prepare a standard set of tools or a corresponding kit.
Step-by-step repair procedure:
- Study the car's manual and determine the key design nuances of the vacuum booster.
- Disconnect the drive rod of the element in question from the brake pedal, which is located under the steering shaft.
- Remove the GTZ in the engine compartment.
- Depending on the malfunction, replace or repair this unit.
The vacuum brake booster provides better dynamics slows down the vehicle and significantly increases the level of comfort of the controls. In practice, the operation of the VUT is reflected by effective braking with minimal pedal pressure. Application active systems help with emergency braking significantly improves road safety.
VUT device
Vacuum booster braking forces in most cars it is located near the engine shield and is a monolithic block with a turbocharger and a brake fluid reservoir.
To enhance the braking force, the VUT design uses:
- metal case;
- a separating diaphragm made of plastic material;
- check valve;
- pedal assembly pusher;
- follow-up valve;
- hydraulic cylinder rod;
- return spring.
Principle of operation
Clamping force brake pads in cars whose design does not require the installation of VUT, it is pumped by the force created by the driver when pressing the pedal. A vacuum brake booster uses differences in atmospheric pressure to create a vacuum, thereby helping to build up pressure in the brake line.
Let's start with the fact that the working diaphragm divides the body into atmospheric and vacuum (located on the GTZ side) chambers. It is connected through a pusher to the pedal. When the brakes are not applied, the follower valve maintains equal pressure in the two chambers. Depressing the brake pedal causes the follower valve to “cut” the connection. Bypass valve equalizes the pressure of the atmospheric part of the body with engine compartment. The vacuum, which has been maintained in the VUT housing all this time, now attracts the diaphragm. As soon as the driver releases the brake pedal, the return spring returns the elastic partition to its original position.
The low pressure in the housing, which drives the vacuum booster, is created through a hose connecting the vacuum part to the intake manifold. It occurs due to the vacuum created by the piston descending to BDC during intake fuel-air mixture. If vacuum gasoline engine sufficient for normal operation of the VUT, then diesel engines V mandatory are equipped vacuum pump, designed to create a vacuum. Depending on the design (petal, membrane), such a device is driven by: injection pump, generator or camshaft. 
VUT breakdowns
Malfunctions of the vacuum booster can affect not only the effectiveness of the braking system, but also the operation of the gasoline engine. The main types of breakdowns include:
- violation of the tightness of the system, damage to the hose ensuring vacuum;
- diaphragm rupture;
- damage to operating valves or related parts (springs, valves).
Failed amplifier brake pressure does not deprive the car of brakes, but can significantly complicate the control of the vehicle.
If you notice changes in the operation of the booster, do not rush to change the hose or repair the brake booster. On some cars, the air recirculation damper in the cabin is directly related to the operation of the amplifier. The symptoms of depressurization of this system are similar to those that appear when the VUT breaks down.
Self-diagnosis
The simple principle of operation allows you to perform diagnostics yourself. Vacuum booster repairs should be entrusted to specialists. Several simple methods will help you determine if the system is working properly:
- After running the engine for a short time, turn off the car and press the brake pedal several times. With a working amplifier, the first press will be light, and all subsequent presses will require effort. Each subsequent pedal stroke will be shorter;
- turn off the engine and wait a few minutes. You can check the VUT for leaks by pulling out the hose that goes to it from the intake manifold. If there is a vacuum, you will hear a pop of escaping air;
- With the engine off, vigorously depress the brake pedal several times in a row. Start the engine while continuing to hold down the pedal. As soon as the engine starts, a working vacuum booster of the brake system will make the pedal “soft” and it will fail;
- One of the most common problems is air leaks. Check the vacuum supply hose for mechanical damage, as well as the tightness of its connection with the body. In this case it may be necessary urgent repairs VUT. This “suction” of air is quite enough to gasoline engine started to triple;
- the engine is switched off. When you press the pedal for the first time, you should hear the sound of air entering the atmospheric part of the body. If there is none, the membrane is torn or the bypass valve is faulty.
The listed signs of a faulty brake booster will help you diagnose and fix the problem as soon as possible.



