Plays an important role. It makes it possible to disconnect the power plant from the transmission, although it is intended for short-term action. This makes it possible to change the gear ratio of the gearbox by engaging certain sprockets - gear shifting. In addition, the clutch allows you to start moving smoothly, as well as disconnect the box from the motor.
The basis of the work of the clutch is the friction force between different materials, in the case of cars - metal and friction linings. But where there is friction, there is increased wear. Wear increases especially when starting off, when the gearbox is connected gradually.
All this leads to the fact that the main elements of the clutch - the discs wear out, their thickness decreases, and the travels of the discs and the release bearing increase. As a result, the clutch is subjected to increased wear, which can lead to complete wear of the driven disc and the need to replace it.
It is interesting that the adjustment of anything in the clutch design itself is not made, everything is done with a switch-on drive. All this is achieved thanks to the use of a membrane spring in passenger cars. For trucks where the drive disc release levers are installed, it is also necessary to adjust the stroke of these levers. That is, the adjustment for a car with such a clutch is made in two approaches - first, the position of the levers is adjusted, and then the drive.
To make it clearer, let's briefly describe the clutch design. This device is housed in a housing installed between the power plant and the gearbox, with the flywheel coming into this housing from the engine side, and the drive shaft from the gearbox side. The end of this shaft enters the flywheel to maintain alignment with the gearbox drive shaft.
The main element of the clutch is the basket with the drive disc placed in it. spring-loaded, but has the ability to move longitudinally due to these springs, as well as levers. In passenger cars, the spring is combined with the levers - a membrane spring.
The basket is bolted rigidly to the flywheel. A driven disc is placed between it and the flywheel. The axis for this disk is the gearbox shaft, and it is connected to it by means of splines along which the disk can move. 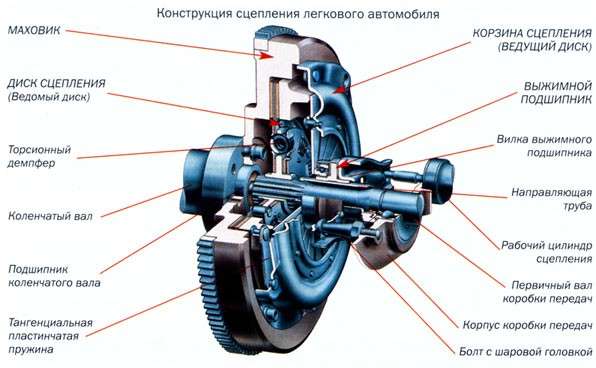
Briefly about the principle of work. Since the basket with the drive disc is rigidly attached to the flywheel, it fully absorbs the engine torque. But the basket is not connected with the box, so it does not convey this moment anywhere. But the driven disc is connected to the box, since it is seated on the drive shaft. To transmit the moment, you need to clamp, and strongly, the driven disc between the drive and flywheel. The springs are responsible for this, which pressurize the driving disc.
If you need to disconnect the engine and the gearbox, you need to act on the springs that press the drive disc. The force decreases, the disc, moving away, stops pressing the driven disc to the flywheel - the transmission of torque ceases to be produced.
That is, in order to disconnect the motor from the gearbox, you need to act on the springs of the drive disc. For this, a release bearing is included in the design. It is located behind the basket on the gearbox drive shaft flange. Moving along this flange, he can act on the springs of the basket, but for this he needs an effort to overcome their resistance. This effort is taken from the foot of the person who presses the clutch pedal. Its force is transmitted through the drive system to the bearing, and the bearing is already in operation.
Clutch pedal free play
As already mentioned, disc wear occurs over time, as a result of which the travel clearances of the discs and bearing change. Therefore, the clutch, or rather the drive, must be periodically adjusted in order to remove the gaps that have appeared. In a passenger car, it all boils down to the fact that only adjustment of the pedal free travel is performed.
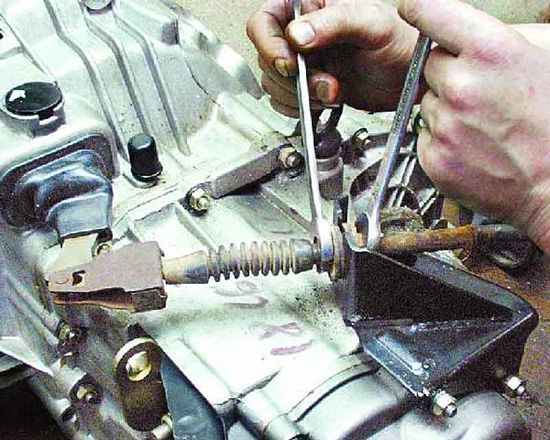

Clutch drive adjustment
This move must be present - this is just a gap between the clutch release fork, release bearing and basket levers, but it is absolutely necessary so that there is no constant contact between the bearing and the levers, which will cause the bearing to work constantly and quickly fail. Also, this gap should not be large, since the clutch pedal travel is limited, and if there is a large sample for free travel, the rest of the pedal travel will not be enough for full squeezing.
Even with normal clutch operation, the pedal free travel should be measured at least once a year. With a normal working clutch, this stroke should be 30-35 mm, regardless of the type of drive - mechanical, cable or hydraulic.
The change in the size of this stroke mainly depends on the driving style of the driver. With an aggressive style, when the clutch is actively used, in particular the friction linings, it is produced faster. As a result, the size of the freewheel will change faster.
Major clutch malfunctions
Video: Malfunction of the clutch on the VOLGA
If you do not pay attention to the work of the clutch at all, then often this leads to the following problems:
- When the pedal is fully depressed, the car continues to move - the clutch "leads". This is precisely due to the wear of the discs, while the gap resulting from the wear is not sampled. The increased free travel leads to the fact that it is not possible to completely disconnect the motor from the gearbox and the torque continues to be transmitted even when the pedal is fully depressed. This is accompanied by a complicated gear shifting, crunching when engaging the gears of the checkpoint;
- The opposite of the situation described is clutch slip. The reason for slipping is the lack of free play and the hauling of the fork position. As a result, the release bearing constantly presses slightly the springs of the drive disc, which is why it does not fully press the driven disc. there is a more difficult set of speed, a specific smell in the cabin due to constant overheating of the linings, increased operating noise due to the constantly rotating release bearing.
- Increased operating noise may also be due to low free play when the release bearing is pressed against the basket levers, but does not squeeze them out. That is, there is no slippage, but the bearing is constantly rotating.
Checking and adjusting the clutch pedal free play
If these signs appear, you should first check the condition of the drive, and then measure the free play. You need to check the connection points of the clutch pedal with the cable, rod or pin of the piston of the master cylinder of the hydraulic drive, and then the connection of the rod, torso or pin of the slave cylinder with the release bearing fork.
Video: How to adjust the clutch actuator
Free play is checked with a regular ruler. One edge of it rests on the floor, and the other is substituted for the pedal. Then lightly press on the pedal, sampling all the gaps from the pedal to the basket levers. In this case, the pedal moves without much resistance. When all clearances are selected, the movement of the pedal will be prevented by the basket springs, the movement of the pedal will be resisted. It is this move before the start of resistance that needs to be measured, it should be 30-35 mm.
If the free play is more or less, adjustment is made. For all cars, with different clutch drives, adjustment is made in one place - the point of connection between the drive and the bearing fork. To do this, there is a thread with two nuts on the pin of the cable, rod or working cylinder. With this pin, the drive enters the fork and is secured with nuts.



