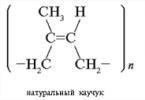
A car is a collection of components and mechanisms designed to ensure movement. vehicle in one direction or another. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of steering control maintenance and repair for the safety of both the owner of the car or its passengers, and for all other road users. Therefore, this system is subject to whole line quite strict requirements. And the repair or maintenance procedure itself is quite strictly regulated.
Main types of mechanisms
On modern cars There are three main types:
- Worm-shaped. They, in turn, are divided into worm-roller and worm-sector types.
- Toothed (rack or gear type).
- Screw, which can be either a screw-lever or a screw-rack element.
- Rear-wheel drive passenger cars are most often equipped with a screw-roller type mechanism.
Of course, depending on the type of system, steering repair in each specific case has its own characteristics, subtleties and nuances. In order to understand all aspects of this complex and labor-intensive process, it is necessary to have not only deep theoretical knowledge, but also rich practical experience, as well as the necessary arsenal of equipment and tools. That is why it is best to entrust car steering repairs to highly qualified specialists. However, there are general principles, algorithms and diagrams used as the basis for carrying out this type of work.
What does it consist of?
Experts usually divide the steering system as a whole into three components:
- steering mechanism, discussed in detail above;
- drive, it can be either front or rear;
- drive booster system (not installed on all models and classes).
In addition, the drive trapezoid can be of two types - threaded or split. Such diversity makes servicing and repairing a car's steering a complex technological process.
Main requirements for the system
The main requirements for the steering of a car and related to safety are the following:
- correct kinematics of rotation, eliminating factors of lateral sliding or slipping;
- ease and simplicity of control;
- ensuring the required gear ratios;
- high strength and rigidity of parts and assemblies;
- tight fit of parts and minimal gaps in joints.
All this requires a scrupulous approach, careful attention to the system and its constant monitoring.  Therefore, maintenance and repair of the steering system are certainly included in the list of mandatory work during TO-1 and TO-2, as well as during the seasonal maintenance course.
Therefore, maintenance and repair of the steering system are certainly included in the list of mandatory work during TO-1 and TO-2, as well as during the seasonal maintenance course.
Types of maintenance
Maintenance of steering mechanisms and components is carried out as planned. Depending on the type of service, one or another amount of work is performed. It is customary to distinguish the following types of complexes of preventive and repair work:
- daily maintenance;
- TO-1;
- TO-2;
- seasonal preventive complex.
Daily set of measures
It is quite obvious that repairing a KamAZ steering control differs significantly from similar work performed on the system of any passenger car.  But as for the daily set of actions, it includes a fairly universal list of measures applicable to vehicles of almost any class. This list includes the following actions:
But as for the daily set of actions, it includes a fairly universal list of measures applicable to vehicles of almost any class. This list includes the following actions:
- steering wheel free play control;
- visual control of the reliability of the steering bipod fastenings;
- checking the functionality of the limiters maximum angles turning;
- checking the size of the gaps in the power steering joints and steering rods;
- general monitoring of the performance of the control and amplifier.
It is important to note that the entire cycle of work listed above is strongly recommended to be carried out with the engine running.
First maintenance
Complex of maintenance and repair works automotive system management in the case of TO-1 includes the following additional actions:
- checking the condition of fastening the nuts and cotter pins of the steering bipod fasteners;
- monitoring the condition of the steering axle levers, as well as ball pins;
- monitoring of free movement of traction joints;
- checking how tight the repair is when problems are detected;
- monitoring the level in the power steering reservoir, topping it up or replacing it when the level drops below the critical level set by the manufacturer.
In addition, a thorough check is made of the tightness of the fastening nuts, the condition of the wedges, pivots and other fastening elements. In addition to this, a more thorough than usual visual inspection condition of parts, components and fastenings of the system.
Second maintenance
During maintenance-2 steering the vehicle is subject to deeper control.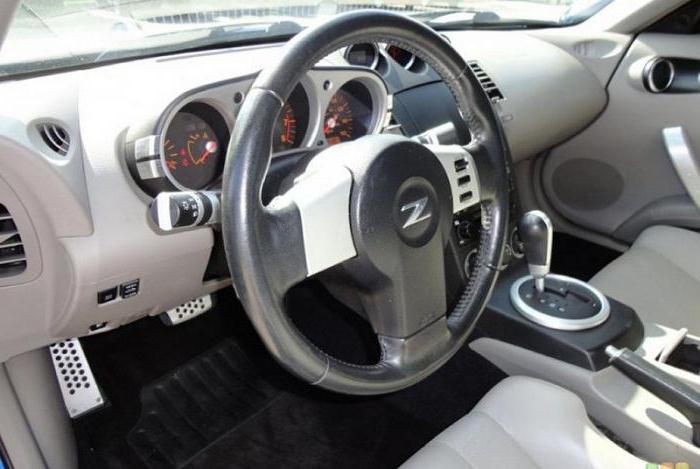  In addition to the actions performed during TO-1, in standard list TO-2 measures, in particular, include the following work:
In addition to the actions performed during TO-1, in standard list TO-2 measures, in particular, include the following work:
- monitoring the correct values of the steering wheel alignment angles and adjusting them if deviations are detected;
- checking the fastening of the steering housing, pivot wedges, as well as all joints of parts and assemblies;
- fastening control cardan shaft steering wheel, traction joints and king pins, clearance values in the steering system;
- diagnostics of the power steering system condition.
Work that involves repairing the steering when secondary maintenance, allow you to avoid most potential malfunctions, malfunctions and problems with vehicle control, providing effective prevention. 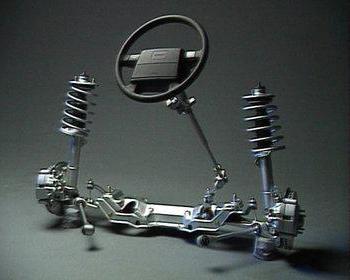 If, of course, they were produced on time and with proper quality.
If, of course, they were produced on time and with proper quality.
Seasonal maintenance
Seasonal maintenance is an additional measure that allows for effective monitoring of the condition and performance of the steering. At seasonal service, as a rule, the same amount of work is performed as during maintenance-2 and is supplemented by work on replacing lubricants and technical fluids according to the season.
Thus, constant monitoring and timely implementation of the necessary set of measures for the maintenance of the vehicle control system can not only significantly increase its safety.  In most cases, it makes it possible to avoid very significant losses, both financial and temporary. As you know, repairing the steering control of MTZ, KamAZ, and any other car, especially modern ones, is quite expensive. By analogy with medicine, maintenance is exactly the case when it is much easier and cheaper to prevent a disease than to treat it later.
In most cases, it makes it possible to avoid very significant losses, both financial and temporary. As you know, repairing the steering control of MTZ, KamAZ, and any other car, especially modern ones, is quite expensive. By analogy with medicine, maintenance is exactly the case when it is much easier and cheaper to prevent a disease than to treat it later.
So, we found out how to repair a car's steering.
Maintenance steering
TO category:
Routine maintenance
Steering Maintenance
Every day before leaving the line you need to check the operation of the steering. At a vehicle speed of 3-6 km/h, turn the wheels from one extreme position to the other in both directions; the wheels should turn smoothly, without jerking, and the force applied to the steering wheel should not be large.
Check the tightness of the connections of the oil lines and hoses and eliminate any oil leaks. Inspect the fastenings of the main components and steering elements: steering mechanism, power steering, levers, rods and steering column; Special attention You should pay attention to the condition of the levers and rods.
Check the oil level in the steering mechanism: it should be 35-40 mm below the outer edge of the filler hole; use a wrench to check the fastening of the steering mechanism to the frame, the cardan shafts on the shafts, inspect the locking of the nuts securing the steering bipod, swing arms and ball pins; Lubricate the distributor ball joint through the grease nipple on the power steering distributor housing.
After 1000 hours (2 times a year when the operating season changes), replace the oil in the steering mechanism: the used oil is drained through drainer and pour 2.8 liters of fresh oil through the filler.
After 2000 hours (40,000 km, but at least once a year), the grease in the steering rod and power steering joints is replaced. In this case, you need to carefully inspect the parts and replace worn ones. When performing this operation, it is necessary to remove the rods and hydraulic booster from the vehicle, disassemble the hinges and wash all parts in kerosene or diesel fuel. During assembly, the hinge cavity and the cavity under the seal are filled with fresh lubricant and the clearance in the hinge joint is adjusted.
When performing work related to changing the lubricant in ball joints, the position of the steering elements may be disrupted, so after performing this operation you should check freewheel steering wheel, toe-in and maximum steering angles.
IN ball bearings During assembly, the steering column was lubricated with CIATIM-201 lubricant. The lubricant should be replaced every time the column is disassembled.
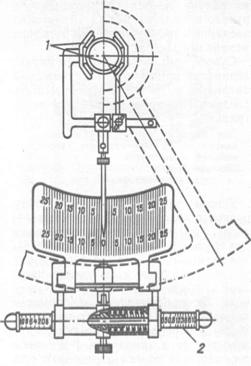
Adjusting the clearances in the joints of the rods, power steering and distributor. To adjust the clearance in the distributor ball joint, you need to disconnect the hydraulic booster and the tip with the joint from the steering rod. Remove the locking plate (see Fig. 33) from the nut slot, applying the necessary force, since the plate is cored. Holding the glass from rotating with a screwdriver, use a special wrench to tighten the nut until it stops, then unscrew it until the slots in the nut coincide with the slots in the glass and lock the nut with a plate. Unscrew the nut and plate.
Checking and adjusting the free play of the steering wheel. The operation is carried out with the engine running, the car must be slowed down by the service and parking brakes.
Sequence of operation: lift the front axle, start the engine and set the wheels in a position corresponding to the vehicle moving in a straight line; attach the play meter scale to the steering column and the arrow to the steering wheel rim; rotate steering wheel to the left to full choice play - before the steering wheels of the car begin to turn, but their position should not change; set the playmeter arrow against zero mark on the scale; turn the steering wheel right side before the steering wheels begin to turn, i.e., until the gaps in all connections are completely selected, and by the relative position of the arrow and the playmeter scale, determine the free play (angle of free rotation) of the steering wheel in degrees.
The angle of free rotation of the steering wheel when the hydraulic booster is operating should not exceed 25°. If the angle is more than 25°, you need to tighten the fastenings of the steering mechanism, steering bipod, swing arms, cardan forks, steering wheel and column. If the free play of the steering wheel does not decrease after this, it is necessary to check the clearances in the hinges. This check is carried out visually: with a sharp rotation of the steering wheel ball pins should not move in the hinges, but in spline connection There should be no noticeable play in the propeller shaft and cardan shafts.
In the steering mechanism, the clearances in the tapered roller bearings and in the rack-and-pinion nut-rack-sector are adjusted.
To adjust these gaps, the steering mechanism must be removed from the car and installed on a special stand.
Before adjusting the gaps in roller bearings it is necessary to unscrew the cap (see Fig. 32) and the lock nut and unscrew the adjusting screw 1.5 turns (rotate counterclockwise) - in the engagement of the rack - sector, the gap will increase and the resistance to the relative movement of the rack nut and sector when turning the screw will decrease.
The rack nut is installed in the steering mechanism in the middle position (full movement of the rack nut on the screw between the bearings corresponds to six revolutions of the screw). The adjusting screw is screwed in until it stops and then backed out approximately 1/4 turn.
Having secured steering bipod motionless, in this position the angular play of the screw is checked using the dial on the stand: the play should not exceed 6°. If the angle is more than 6°, adjust the gap in the engagement of the nut - rack and sector with an adjusting screw.
With correctly adjusted clearances in the bearings and rack gearing, the angular play of the screw in the middle position of the rack nut will be 6° with the steering bipod fixed. If the angular play of the screw is still greater than 6°, it is necessary to adjust the end gap between the screw head and the sector. Then you should drain the oil from the steering mechanism. Unscrew the cover mounting bolts and, turning the screw clockwise, remove the cover from the sector shaft. Cut off the stopper (welding) in the sector-nut connection, screw the nut all the way, make a common narrow mark on the sector and the nut and unscrew the nut in the opposite direction by 6 mm around the circumference of the nut thread and lock it in this position with the welding point: end gap at connection sector - the adjusting screw will be equal to 0.1 mm. Secure the cover in place and adjust the gap in the engagement of the rack nut and sector as indicated above.
Adjusting the power steering safety valve. The valve is factory adjusted and sealed.
If its adjustment is still necessary, then this operation is performed on a special stand. You can also adjust the valve on a loaded car: connect a pressure gauge (via a special adapter) to the discharge line from the automatic pump switch to the hydraulic booster. After starting the engine, heat the oil in the system to a temperature of 30-35 ° C, then set the rotation speed to a constant crankshaft engine 1600--1700 rpm (for the BelAZ-540 car - 1300-1350 rpm). Turn the steering wheel to the right until the valve is activated - the wheels will stop turning. If the wheels turn but the valve does not operate, loosen the valve spring so much that when the wheels turn the oil pressure is 80-85 daN/cm2. If the oil temperature has risen to 50” C, adjust the valve to a pressure in the line of 72-77 daN/cm2.
When performing this operation, the vehicle must be braked with the parking and service brakes, and under rear wheels put special pads. All other adjustment operations are performed only when the engine is not running.
In case of CO, change the oil while simultaneously flushing the crankcase (reservoir and filters of the power steering pump of the ZIL-130 car) with gasoline in accordance with the time of year.
Typical steering malfunctions are: – increased free play of the steering wheel and longitudinal movement (play) of the column shaft due to wear of the parts of the hinge joints of the steering rods and levers, loosening of the fastenings of the steering gear housing to the frame, the rotary levers to the axles; – wear of the working pair of the steering mechanism or tapered bearings of the steering shaft; – knocking and play detected when the suspended front wheels of the car sway, due to wear of the axle bushings or king pins; – difficulty turning the steering wheel due to jamming in the pins or steering mechanism; – increased noise during operation of the power steering pump caused by insufficient level
oil in the pump reservoir, weak pump belt tension, presence of air in the system; – lack of effort when turning at various engine crankshaft speeds due to sticking of the pump spool, unscrewing of the pump safety valve seat, clogging of the drain or pressure lines of the hydraulic booster.
You should promptly lubricate the hinge joints of the rods, levers, steering driveshaft, as well as the steering mechanism with appropriate lubricants and make the necessary adjustments. Before adjusting the steering, check the gaps (play) in the hinge joints of the longitudinal and transverse steering rods, independent suspension, axial play of the steering shaft, gaps in the engagement of the working pair of the steering mechanism, etc.
The clearances in the steering linkage joints are checked by sharply rocking the steering wheel in both directions. In this case, a significant movement of the longitudinal steering rod relative to the pins will indicate the need to eliminate play in the articulated joints of the rods. To do this, unscrew the adjusting plug at the end of the rod, screw the plug with a special spatula until it stops and unscrew it so that the slot in the plug coincides with the hole for the cotter pin, and then tighten it. In the same way, play is eliminated in the other articulated connection of the rod.

Rice. 108. Backlash meter and device for measuring the pressure of the power steering pump:
a – placement of the play meter on the steering wheel when measuring wheel play; 1 - pointer; 2 – scale; 3 – dynamometer; b – device for measuring the pressure of the power steering pump: 1 – reservoir; 2 – pressure gauge; 3 – valve; 4 – power steering
Axial play of the steering column shaft occurs as a result of wear of the tapered bearings of the steering worm. To check the play, hang the front wheels, put them in the position of straight-line movement of the car, turn the steering wheel to the left one turn and secure it in this position, then cover steering column with your left hand and bring your thumb to the joint between the bottom of the steering wheel hub and the steering column casing; rocking the front wheels in different directions, check by touch the axial play of the steering column shaft; Feeling the axial play with your thumb will indicate the need to adjust the steering gear bearings.
To check the clearance in the engagement of the working pair of the steering mechanism, unscrew the plug of the hinge joint of the longitudinal rod and remove the rod from the ball pin of the steering bipod with the front wheels in a position corresponding to the straight-line movement of the car, then measure the force required to rotate the steering wheel using a play meter with a dynamometer.
For vehicles with a hydraulic booster built into the steering mechanism (KamaE-5320, ZIL-130 and their modifications), steering play is determined only when the engine is running at low speeds in the idle move. Correct operation of the hydraulic booster specified vehicles is ensured if its pump develops a pressure of at least 6 MPa.
If the readings of the dynamometer or control pressure gauge do not meet the specified standards, then the steering should be adjusted.
Typical failures and malfunctions of the steering are: loosening of the steering gear housing, increased wear parts of the steering mechanism, ball joints of rods and levers, loosening of the steering wheel and steering column, chipping of the worm pair and incorrect adjustment(excessive tightening of parts) of the steering mechanism.
Malfunctions of the power steering are: insufficient or too high level oil in the pump reservoir, presence of air (foam in the oil reservoir) or water in the system, pump malfunction, increased oil leakage in the steering mechanism, clogged filters, malfunction bypass or safety valve of the pump (periodic freezing, sticking, loosening of the seat), insufficient tension of the pump drive belt.
These malfunctions lead to an increase in the free play (play) of the steering wheel, the effort to turn the steering wheel rim when turning, knocking in the steering mechanism, the appearance of oil from the pump breather (power steering wheel), etc. The steering mechanism may become stuck or jammed.
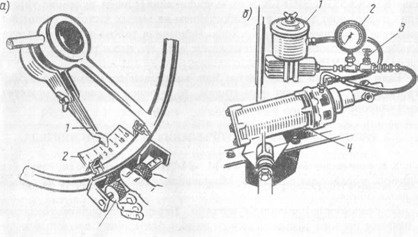
The force applied to the steering wheel rim with the wheels hanging must be within the limits for trucks 30-40 N, for cars - 7-12 N. They also check the fastening and condition of the steering linkage joints. The play is determined using a dynamometer-play meter (Fig. 30.26), mounted on the steering wheel rim with clamps 1. The angular movement of the wheel is determined under the influence of a force of 10 N applied to the dynamometer 2. On vehicles with hydraulic power steering, the play is measured with the engine running.
Definition total play does not give an idea of what connection or assembly caused its increase, unless you first check and tighten the steering gear housing and steering bipod; eliminate gaps in the steering rod joints; Check the air pressure in the tires and the adjustment of the wheel bearings.
During EO, check the tightness of the hydraulic booster connections. Make sure there are no fluid leaks. If necessary, tighten the fastenings. Check the condition of the steering drive by external inspection, making sure that there are cotter pins, nuts on the hinge pins and that the rods are not bent.
During TO-1, the steering mechanism is controlled with a dynamometer-backlash meter when the vehicle track is in a straight position. The efforts to turn the steering wheel are monitored with the front wheels hanging out.
They check and, if necessary, eliminate play in the hinge joints of the steering rods. It is more convenient to check the play with two people: one sharply turns the steering wheel to the right and left, and the other looks at the movement of the hinge joint. If one part of the connection moves and the other is stationary, then there is play; if both parts move simultaneously, then there is no play.
You can also determine the play in the hinge joints by moving the rod with your hands in the longitudinal direction. If, for example, the longitudinal rod moves along with the bipod, then there is no play in the hinge joint. To adjust the play, you need to unsplit the plug and tighten it with a special wrench until there is noticeable resistance, and then unscrew the plug to the first position at which it can be splinted.

Rie. 30.26. Dynamometer-backlash meter
Check the cotter pin nuts of the ball pins by inspection and, having removed the cover of the power steering reservoir, check the oil level in it and the oil level in the steering gear housing, top it up if necessary,
Check and, if necessary, adjust the tension of the power steering pump drive belt (deflection under a force of 40 N should be no more than 8-14 mm).
During TO-2, the steering wheel fastening is checked. The steering wheel is slightly moved along the shaft or rocked in a direction perpendicular to the plane of rotation of the wheel. If any loosening is detected, remove the horn button and tighten the wheel nut on the steering shaft with a spanner.
The axial clearance in the roller bearings of the steering gear worm is usually adjusted using shims located under the lower cover of the steering gear housing.
The steering mechanism of a ZIL-130 car with hydraulic booster is adjusted based on the results of force measurements using a spring dynamometer on the steering wheel rim in three positions: - in the first position, the steering wheel is turned more than 2 turns from the average position (at which the car moves in a straight line); in this case, the force should not exceed 5.5-13.5 N; – in the second position, measure and note the force value when turning the wheel 3/4 - 1 revolution from the middle position; – in the third, when passing through the middle position, the force should not exceed by 8-12.5 N the value obtained when measuring in the second position and should not be more than 29 N.
Begin adjusting the steering mechanism based on the results of the third position using the adjusting screw for the axial movement of the bipod shaft. The discrepancy between the force values in the first and second positions is a consequence of wear ball nut or screw. In this case, the adjustment is performed with the steering mechanism removed from the vehicle.
After adjusting the engagement of the roller and the worm of the steering mechanism, use a dynamometer to check the force required to turn the steering wheel. This force (with the steering rod disconnected), measured with a spring dynamometer, should be passenger cars 7-12 N, for trucks - 16-22 N when passing through the middle position of the steering wheel,
In case of CO, change the oil while simultaneously flushing the crankcase (reservoir and filters of the power steering pump of the ZIL-130 car) with gasoline in accordance with the time of year.
TO Category: - Routine maintenance
Maintenance of steering mechanisms is planned. The scope of work performed is determined by the type of maintenance. During daily maintenance, it is necessary to check the free play of the steering wheel, the condition of the bipod mounts, as well as the limiters of the maximum steering angles. In addition, it is necessary to check the clearance in the power steering joints and steering rods daily, as well as the operation of the power steering and steering. These checks are performed with the engine running.
During the first maintenance (TO-1), it is necessary to check the fastening and cotter pins of the bipod nuts, ball pins, and steering axle arms; free movement of the steering wheel and steering rod joints; condition of the pins and lock washers; tightening the nuts and wedges of the steering drive shaft; tightness of the power steering system, as well as the level lubricant in the power steering reservoir, top it up if necessary.
During TO-2, the same work is performed as during TO-1, and also checks the angles of the front wheels and, if necessary, adjusts them; check and, if necessary, tighten the fastening of the pin wedges, steering gear housing, and steering column of the steering wheel; clearances of steering, steering rod joints and pivot joints; condition and fastening of the steering driveshaft; fastening and tightness of components and parts of the power steering.
During seasonal maintenance, they perform maintenance work 2, and also carry out seasonal replacement lubricant.
Visual control technical condition parts, assemblies and steering mechanisms are performed by inspection and testing. If access to the steering parts is not possible from above, then the inspection can be carried out above the inspection hole.
Control of the fastening of the column and steering mechanism is carried out by applying forces in all directions. During such a check, axial movement or rolling of the steering wheel, pads, as well as the presence of knocking in the steering components is not allowed.
When checking the fastenings of the steering gear housing, as well as the steering axle levers, it is necessary to turn the steering wheel about neutral position 40-50° in each direction. The condition of the steering drive, as well as the reliability of fastening of the connections, is checked by applying an alternating load directly to the drive parts. The operation of the turn limiters is checked visually by turning the steered wheels in different directions until they stop.
In order to check the tightness of the connections of the power steering system, it is necessary to hold the steering wheel in its extreme positions with the engine running. In addition, checking the tightness of the connections of the power steering system is carried out in a free position of the steering wheel. Connections are considered tight if there is no leakage of lubricant. In addition, when checking, spontaneous rotation of the steering wheel with power steering from the neutral position to the extreme position or vice versa is not allowed.
The friction force, as well as the free play of the steering wheel, is checked using a special device, which consists of a dynamometer and a playmeter. The playmeter includes a scale that is attached to the dynamometer and an indicator arrow that is attached to the steering block using clamps. The dynamometer is attached to the steering wheel rim using clamps. There is a dynamometer scale on the handle of the device. When measuring the steering wheel play, a force of 10 N is applied to the instrument handle, which acts in both directions. After this, the instrument arrow shows the total amount of play. For passenger cars, the total amount of play should be within 10°, and for trucks - within 20°. On vehicles equipped with a hydraulic booster, the play is determined with the engine running.
The total friction force is determined with the front wheels fully suspended. If the steering is correctly adjusted, the wheel should turn freely from the middle position to move in a straight line with a force of 8-16 N.
The condition of the steering rod joints is assessed visually by applying force to the steering wheel. Backlash in the hinges manifests itself in the relative relative movement of the parts being connected.
Checking the power steering carried out by measuring the pressure in the hydraulic booster system. To check, you need to insert a pressure gauge with a tap into the discharge line. Pressure measurements are made with the engine running at low speeds, turning the wheels to their extreme positions. The pressure developed by the hydraulic booster pump must be at least 6 MPa. If the pressure is less than 6 MPa, then it is necessary to close the tap, after which the pressure should rise to 6.5 MPa. If after closing the tap the pressure does not rise, it means that the pump has broken down and needs to be repaired or replaced with a new one.
Adjustment work on the steering mechanism includes work on adjusting the axial clearance in the gearing, as well as in the propeller shaft bearings.
The steering mechanism is considered to be in good condition and suitable for further use if the steering wheel play when driving in a straight line does not exceed 10°. If the backlash exceeds valid values, then it is necessary to check the clearance in the propeller shaft bearings. If the bearings have enough big gap, then the axial play will be easily felt.
In order to eliminate play in the shaft bearings, it is necessary to unscrew the bolts, remove the steering gear housing cover and then remove one adjusting shim. After removing the gasket, the end play check must be performed again. The operation must be repeated until the force to turn the steering wheel is 3-6 N.
The engagement of the screw (worm) with the roller is adjusted without removing the steering mechanism. To do this, you need to unscrew the nut from the screw shaft pin, then remove the washer from the pin, then use special key turn the adjusting screw several notches in the lock washer. As a result of this, the amount of lateral clearance in the engagement changes, which, in turn, changes the free play of the steering wheel.
In order to determine the amount of play in the joints of the steering drive, it is necessary to sharply shake the steering wheel bipod when turning the steering wheel. After checking, tighten the screw plug if necessary. In addition, when checking the axial play, lubricant is added to the joints, and if there is significant wear, the ball pin or the entire rod assembly is replaced.
The main malfunctions of the control system include: breaks and cracks on the crankcase mounting flange, wear of the hole in the crankcase for the steering arm shaft bushing and parts of the ball joints of the steering rods; wear of the worm and roller of the bipod shaft, bushings, bearings and their landing places; bending of rods and loosening of the steering wheel on the shaft.
If the working surface is significantly worn or the hardened layer is peeled off, the steering wheel worm is replaced with a new one. If there are cracks on the surface of the shaft roller, replace it with a new one. The worm and roller must be replaced at the same time.
Worn bipod shaft journals are restored using chrome plating and subsequent grinding to the nearest repair size. The shaft journal can be restored by grinding the bronze bushings installed in the crankcase to the nearest repair size.
Worn bearing seats in the steering housing can be restored using an additional bushing. The bushing is pressed into the worn seat of the bearing, then the bushing is bored to the working size of the bearing.
Broken parts and cracks on the crankcase mounting flange can be eliminated by cooking with a gas flame. Worn hole in the crankcase it is bored to the repair size.
Besides rapid wear Ball pins and tie rod bearings are affected. Thread breakage often occurs at the ends of tie rods. In addition, during operation, springs weaken or break, as well as a violation of the bending of rods.
Worn ball pins that are chipped or scored must be replaced with new ones. Simultaneously with the replacement of the ball pins, their liners are replaced. Broken or weakened springs cannot be repaired and must be replaced with new ones. Violation of the bending of the rods is eliminated by straightening the rod in a cold state.
The main malfunctions of the hydraulic booster are the lack of gain at any engine speed, as well as uneven or insufficient gain when turning the steering wheel in both directions.
In order to eliminate malfunctions of the hydraulic booster system, it is necessary to drain the oil from the system, thoroughly rinse its constituent parts, and also disassemble the pump.
The sequence for disassembling the hydraulic booster pump is as follows:
1) remove the tank and filter cover;
2) holding safety valve to prevent it from falling out, it is necessary to remove the reservoir from the pump body;
3) remove the distribution disc;
4) remove the stator, having previously noted its position relative to the distribution disk and the pump housing;
5) remove the rotor assembly with blades.
In addition, when repairing the hydraulic booster pump, it is necessary to remove the pulley, retaining ring and pump shaft with the front bearing.
The pump parts must be washed with a solution, washed with water and then blown with compressed air.
Free movement must be checked during maintenance bypass valve in the pump cover, as well as the absence of scoring or wear on the end surfaces of the rotor, housing and camshaft.
After inspection, troubleshooting and assembly, the pump must be bench tested. After checking, repairing and monitoring the parts, the steering mechanism is assembled, adjusted and tested with the hydraulic booster assembly.
In addition, due to malfunctions in the steering system, a knocking sound while driving, unstable vehicle movement, and heavy turning of the steering wheel may occur.
If the steering wheel is difficult to rotate, it is necessary to check the pressure in the tires of the front wheels. Another reason for a hard-to-rotate steering wheel may be deformation of the steering gear parts. In this case, you should check whether the steering rods and steering arms are bent and replace the deformed parts.
When turning the steering wheel tightly, you should also check the oil level in the steering gear housing and, if necessary, top it up to normal. If the inspection reveals a faulty oil seal, it must be replaced with a new one. In addition, in some cases, the cause of tight rotation of the steering wheel in the cold is thickening transmission oil. Need to check ball joints steering rods, moving the rod tips along the axis of the fingers. To check, use a lever and a support to move the tip parallel to the axis of the fingers. If the pin liner is not jammed in the socket of the rod tip, the axial movement of the tip relative to the pin is 1-1.5 mm; if the liner is jammed, then it must be replaced along with the liner.
Additionally, the steering wheel may be difficult to turn after repairing the swing arm. This may occur due to an overtightened adjusting nut when replacing the bushings or the swingarm shaft. If the nut is not tightened correctly, the pendulum arm will rotate horizontally under its own weight. If the nut is tightened correctly, the lever will turn only under the influence of force applied to its end.
If the nut is overtightened, you need to unscrew it, then lift the washer and tighten the nut again. After the nut is corrected, you need to connect the ball pins of the rods to the lever.
If there is no problem with the steering mechanism, then the problem lies in the alignment of the front wheel angles. The alignment of the front wheels must be checked after repairing or replacing parts of the front suspension, as well as after driving on rough roads. However, it must be taken into account that precise adjustment of the angles of the front wheels can only be done at a service station.
Knocks from the front suspension while driving, oscillations of the front wheels, and difficulty steering the vehicle may appear as a result of increased gaps in the connection of steering parts due to wear of parts, loosening of the nuts securing the ends or ball pins. In order to eliminate the gaps, it is necessary to tighten the steering rod ball pin nuts, the adjusting nut of the pendulum arm axle, the swing arm ball pin nuts, as well as the steering gear mounting bolts and the pendulum arm bracket. In addition, to eliminate noise, you need to adjust the engagement of the roller with the worm or the worm bearings.
If there is a sharp deterioration in the vehicle's stability, it is necessary to stop and check the fastenings of the steering housing, the pendulum arm bracket, the steering column shaft bracket to the body, as well as the tightness of the ball pin nuts.
If, while driving, the car’s steering wheel “pulls” to the side, then the problem is most likely a drop in pressure in one of the front wheels, so the car deviates in its direction. If the pressure drops in one of the rear wheels The car, even at low speed, begins to drive in one direction, then in the other.
If the vehicle constantly veers to one side, it may be due to deformation of the steering axle or steering arm due to fast movement on a rough road. In this case, the car constantly skids. To check the technical condition of the axle and levers, you must contact a service station. If these parts are so deformed that they cannot be restored, then these parts must be replaced with new ones.
5 rating 5.00 out of 5 (3 votes)