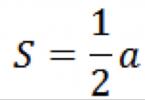This article is about depreciation. vehicle. What is this procedure, why is it necessary, and how is it carried out - further. Full cost purchased vehicle is not immediately written off.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical solutions legal issues but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and IS FREE!
It is deducted gradually, over the course of time. beneficial use. Depreciation is calculated both in tax and in accounting. It is important to have an idea of how to properly depreciate.
General information
Car depreciation is carried out with the aim of writing off its value in parts when they have worn themselves out. It is considered if - the organization has purchased a vehicle or an employee has been hired with his own transport.
When calculating depreciation, you must follow the rules:
| The organization chooses the method | It must be specified in the accounting policy |
| The method that was chosen | Used for the entire useful life of the asset |
| Payments are made every month | In the amount of 1/12 of the total amount for the year |
| Calculation start from the month | Which follows after the vehicle has been put into service |
| If the object is fully depreciated | There is no need to accrue depreciation on it (if the car is used further, then it is simply debited from the balance of the organization) |
| Accrual displayed | By loan 02 |
It is necessary to determine the service life of cars before full depreciation is charged.
There are several payment methods:
- linear;
- diminishing balance;
- writing off in proportion to the amount of work performed;
- accelerated method.
The simplest is linear. Calculated using a simple formula. Consider an example - a company purchased a vehicle worth 500,000 rubles with a service life of 10 years.
Divide 500 thousand by 10, it turns out 50,000. That is, every year the cost of a car decreases by 50 thousand rubles. This method has the disadvantage that it does not take into account all the costs of the car, so the results may be inaccurate.
Depreciation is calculated in such cases:
- if a private entrepreneur or legal entity submits documentation to the tax service;
- when assessed by insurers real value vehicle;
- using personal car at work;
- during the lease.
Depreciation deductions are of several types - physical and moral. The first is to change the value of the vehicle during its use.
It is influenced by mechanical influences, natural phenomena and other factors. The reason for obsolescence is the emergence of newer technologies.
To determine depreciation, you need to know its mileage. To calculate it, you need to know several indicators:
- the cost of all the materials that went into maintaining the car in working condition. The data is taken for the year;
- the cost of the replaced fluid;
- information about the cost of oil.
For the correct calculations, you can write down all expenses in a notebook. In tax accounting, the amount of accrued depreciation on a vehicle is included in indirect costs.
What it is
Vehicle depreciation is the reimbursement for the wear and tear of a vehicle in monetary terms. The car has a useful life.
As soon as the vehicle wears out, depreciation is charged. In the course of its implementation, it is established whether the car can be used further or written off.
Purpose of the procedure
Information about depreciation makes it possible to set the time and frequency of the car inspection outside the plan with maximum accuracy.
Also, depreciation is necessary to establish the period of further use of the vehicle. With the help of this process, the finances that were spent on the purchase of the vehicle are reimbursed.
Legal framework
Depreciation is calculated on the basis of .
Depreciation passenger car depends on its class. Passenger models have 5 of them - the first 4 depend on the engine size.
Classification:
If the car is class 1-3, then the depreciation period is from 3 to 5 years. For vehicles of 4 groups - up to 7 years.
A car of a large and higher class is included in category 5, they have a period of up to 10 years.
For such cars, engine size is not important. Group 5 can include any light vehicle - there are no criteria for assignments in legislative acts.
Employees of the tax office refer to this class cars with a popular brand, high price, size - sedan, limousine and others.
In vehicles of a domestic manufacturer top class indicated by the number 5 in the model number (it will come first).
There is no classification by class in foreign cars, therefore, when determining the depreciation period, you should rely on the conclusion from the manufacturer.
When calculating the depreciation factor, the following indicators are taken into account:
- the age of the vehicle;
- current mileage;
- manufacturer;
- operating conditions, frequency of use, climate;
- ecological situation in the area of use;
- the use of the car is a city, village or town.
If the vehicle is no more than 5 years old, then the formula is much simpler - depreciation costs will be 15% -20% per year.
Truck
When an organization purchases a vehicle and defines it as a freight vehicle, the next step is to establish its useful life. When assigning a truck to a particular depreciation group, a number of factors are taken into account.
The classification of the depreciation group of trucks is as follows:
Freight road transport includes trucks, vans, tractors, trailers.
When leasing
- a popular and demanded procedure. This is the most convenient form of purchasing a vehicle.
Depreciation deductions are applicable only to subjects of financial and economic activity, individuals they don't touch. accelerated depreciation makes it possible to write off funds faster, replace them with new ones.
Leasing has advantages and disadvantages. The first ones are:
- minimal ;
- reduction of the tax base;
- the opportunity to buy the leased object at the final price.
When determining the tax base, the basis is the residual value. With accelerated depreciation, it will decline faster.
When accepting a car under leasing, the recipient must establish the useful life. The term may be specified in the contract.
In other cases, the organization sets it on its own. Depreciation starts from the moment the car is put into use.
Life time
service life and warranty period- the concepts are different, do not confuse them. According to the law, the service life is the period during which the vehicle manufacturer is obliged to fulfill the following:
- ensure the possibility of using the car for its intended purpose;
- responsible for the shortcomings caused by his fault.
The buyer during the entire service life has the right to expect the following:
- vehicle maintenance and repair;
- setting requirements regarding the quality of the car;
- compensation for harm.
Since the truck is a working category of transport, its service life is measured not in years, but in kilometers.
To increase the service life you need:
- undergo a technical inspection in a timely manner;
- do not overload transport;
- use high quality lubricants;
- in time to change the oil;
- replace candles, filters and other materials;
- buy high quality parts;
- undergo service in special centers.
The service life of a passenger car depends on the conditions of its use. The operating period can last up to 15 years. Foreign cars can last longer, cars domestic manufacturers- no more than 8 years.
Every vehicle needs consumable which needs to be changed periodically. Both the comfort of the ride and the life of the owner of the vehicle depend on its condition.
The more the car travels, the longer its service life. All vehicle components also have their own service life. As soon as they wear out, they need to be replaced.
Generator
The alternator affects the performance of the battery. Its service life is much less than that of the engine - about 160,000 km.
shock absorbers
The shock absorber is affected bad road And fast driving. As a result, the part is destroyed. In cars of domestic manufacturers, the serviceability of a part can last for 30,000 km, in foreign cars - up to 70,000 km.
battery
A modern vehicle is equipped with a battery. He charges electrical energy all vehicle systems.
Like any other part, a battery has a lifespan. On average, under normal conditions of use, the period is up to 5 years.
To extend the deadline, you must do the following:
- do not use a discharged battery;
- facilitate starting the engine;
- do not discharge the battery during start-up;
- undergo regular maintenance;
- turn off electrical devices when the vehicle is not moving.
A radiator is needed to cool the engine. Its service life is insignificant - no more than 2 years. Once a year it is necessary to inspect the radiator, as it can wear out ahead of time.
tires
Often, business leaders are interested in what constitutes accelerated depreciation. Consider the main features of such accruals, the main advantages and disadvantages, as well as the methods used in 2019.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to solve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and IS FREE!
An enterprise that has intangible assets and fixed assets must accrue depreciation. In certain situations, accelerated depreciation methods may be used. Let's define the main nuances.
Basic moments
There are two depreciation methods. In the first case, depreciation is charged in equal parts over a certain period. In the second case, accelerated depreciation is used. Consider what its essence is and what functions.
Required terms
Depreciation is a decrease in the primary price of an object during wear in the production process or during obsolescence. Depreciation is reflected every month at depreciation charges.
Depreciation is the gradual wear and tear of an object and the transfer of their price evenly to the goods produced. The accrued depreciation amount is included in the cost of goods that are produced, or distribution costs.
They create depreciation funds that are used during restoration work. A common technique that provides faster asset taxes is accelerated depreciation.
With its help, owners can get more income to recover costs at certain stages of the development of the enterprise.
The use of specific forms of depreciation is based on finding ways to reduce the tax burden on the firm. Accelerated depreciation is called at an inflated rate, when an increase in the rate is permissible no more than 2 times.
That is, most of the asset price is written off as expenses in the first years of using the facilities, and this will allow managers to reduce profits.
Direct depreciation mechanisms are not applied here. But this will also affect the ability to claim depreciation of objects in the coming years.
Functions performed
The task of depreciation is to allocate the price of tangible assets that are used for a long time to costs over operating period.
The basis is the use of systematic and rational records. There is a distribution procedure, not evaluation.
Accelerated depreciation allows you to stimulate the pace of development of the industrial sector.
In Excel, when calculating accelerated depreciation, the following functions are used:
The legislative framework
When determining depreciation charges, one should be guided by the following regulations:
Features of the procedure
Depreciation accounting is a way to reduce a firm's taxes.
With inflation, the straight-line depreciation method can lead to an increase in the tax amount from the company, which means that it is more expedient to apply the accelerated depreciation method.
It should be noted that accelerated depreciation is not charged:
With this type of depreciation, several methods for calculating depreciation amounts with increasing coefficients (but not more than 2) are used. Due to the accelerated type of depreciation, the main cash can write off faster.
When calculating depreciation, you need to use the method:
- discrete depreciation (write-off methods taking into account the period of work);
- diminishing balance;
- degressive geometric damping.
Accelerated depreciation is applicable to leased assets. Then the index of the coefficient is no more than 3.
Due to accelerated depreciation, the tax on property objects and on is reduced, but the leasing discount is kept in active modes.
At the end of the leasing contract, lessees can buy the object at a small residual price. The benefit is that the person has to pay a small amount at the end of the terms. Let's take a closer look later.









Applied methods
There are such ways to determine the depreciation charge for specific objects:
- linear;
- writing off prices in proportion to the volume of goods;
- write-offs of the price by the sums of numbers of years of the period of useful life;
- reduced balances.
The last two methods are used in accelerated depreciation. Assets wear out faster the first time they are used, which means that depreciation charges will be smaller over time.
There is also such a division of methods:
- a double remainder that decreases;
- sum of years;
- one and a half declining remainder.
If the assets were put into operation later than 1986, then depreciation is carried out taking into account the operating period and other factors using the methods of straight write-off, one and a half or double balance, which decreases.
The most accelerated depreciation in accounting is represented by the simplest formula. For example, objects that have a service life of 4 years will have the following sum of years:
So, in the first year of use, deductions for depreciation will be 4/10 of the price of equipment, in the second - 3/10, etc.
When using the declining balance method, the deduction percentages should be determined according to the straight-line write-off method. The figure is then doubled for the first year.
For the second year, depreciation is determined by multiplying twice the percentage by the price that is not written off. As a result, the amount of deduction for depreciation will be less than with the straight-line write-off method.
Under the unit-of-operation method, firms must change the deduction rate in proportion to the intensity of use of assets in reporting periods. This flattens out the income.
Fixed assets
The list of objects in respect of which the accrual of accelerated depreciation is possible is in Art. 259.3 NK.
This applies to:
The cost of purchasing and creating OS, the environment of which is aggressive, can be written off as a reduction in taxable income 2 times faster (). The coefficient is set to 2.
For the right to apply accelerated depreciation, one condition must be met - to use the object in an aggressive environment, when the operating system wears out faster, or to use the object in an environment that is equivalent to aggressive.
For example, the OS may come into contact with such an environment, as a result of which there is a risk of emergencies. But you cannot apply the accelerated depreciation method with respect to objects 1, 2, 3 of the depreciation group.
Motor transport
For example, an organization draws up a leasing agreement, the subject of which is crane. The book value will be reduced 3 times faster than in cases where the object is purchased on credit or for its own funds.
After a few years, you can pay several times less for transport in order to redeem it. But keep in mind that while you are operating the car by, it will not be put on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
And when buying at a residual price (75-25% of the primary price), it will also be reflected in the declarations. As a result, and will be reduced.
Depreciation is not accrued when repairing or upgrading an object. The accrual of depreciation amount for up to a year is terminated.
Such amounts are not charged when the vehicle is transferred for use free of charge, or when the vehicle is conserved for a period of more than 3 months.
With the reducing balance method, larger depreciation amounts are written off at first compared to later accruals. First determine the annual amount of deductions. At the same time, residual fixed asset prices at the beginning of the year are taken into account.
The depreciation rate can be increased by acceleration factors that are set by the federal ministry and department in the list effective form machines for the high-tech industry.
Leasing coefficient
The use of accelerated depreciation in leasing is the main advantage of financing under a leasing agreement. But how exactly does the mechanism for calculating OS depreciation work in this case?
Advantages of using the accelerated type of depreciation in leasing:
The basis for establishing the property tax base is residual price indicators. It is possible to completely write off fixed assets when using accelerated depreciation from coefficients up to 3 three times faster.
When leasing deal ends and the leasing object is fully written off, depreciation on it is not included in the costs, while with ordinary depreciation charges, the fixed asset is depreciated, reducing the tax base.
Using accelerated depreciation, it is necessary to control the overall cost indicators and financial results of the enterprise, a significant amount can lead to a loss during the period of depreciation, which is considered as a disadvantage of using such a mechanism.
Compiled for the period during which it is possible to write off the leased item using accelerated depreciation methods.
For example, if an object belongs to 5 depreciation group, which has a useful life of 7-10 years, the accelerated type of depreciation will allow you to write it off in 3 years.
After this period, the indicators redemption value will be minimal.
At this price, the object will be reflected in the lessees' own fixed assets. The zero value of the residual value is beneficial for lessees when selling repurchased objects.
When calculating the accelerated depreciation of leasing objects, the following formula is used:
So, the coefficient cannot be more than 3. This rule does not apply to the depreciation group 1-3.
If the leasing object is used under a contract that was drawn up before the beginning of 2002, depreciation is calculated according to the following rules:
Benefits of using accelerated depreciation for environmental protection equipment
For example, the firm has acquired new vans. The main advantage of the accelerated depreciation method is the possibility in the first year of use of objects to carry out standard price depreciation using tax deduction.
The alternative is accelerated deductions and the application of most of the capital over the next few years. Minus - the price of vans will not be generated from the tax deduction in the remaining years.
The end result is that the company is provided with a good tax and it receives new objects in one tax year.
With accelerated depreciation, you can increase your investment within the enterprise, which consists of net income and depreciation.
Such investments are always available and can be disposed of by the organization. They have no price - they are free for the company.
The disadvantage of the accelerated type of depreciation is that you need to be careful. At first glance, this is a great way to get the maximum return on assets in the early periods.
But there is a risk that its use will lead to a financial problem at other times. Before deciding on the use of accelerated depreciation methods, it is worth checking other possibilities for solving problems.
Sometimes accelerated depreciation brings more problems. That is why it is better to consult a financial analyst or contact an accounting organization.
What about conservation funds? The methods of accelerated depreciation of such funds are a globally proven measure to stimulate the priority type of work, the scientific technical process.
The company, by overestimating depreciation, can reduce the amount of income that should be taxed. As a result, net income increases.
Experience in the use of depreciation for environmental purposes in different countries shows nice results– capital is quickly accumulated for equipment renewal, environmental damage is minimized.
An entity may apply the accelerated depreciation method if certain conditions are met and the law is complied with. When this method is appropriate, and when it only brings problems, we found out.
It's up to you to fulfill the requirements normative documents when making calculations. After all, the rules for determining the wear of objects should still be observed unconditionally.
Attention!
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the site.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee the solution of your specific problems.
Therefore, FREE expert consultants are working for you around the clock!
In this article we will consider: depreciation of vehicles. We will find out what applies to the vehicle and talk about the norms of the vehicle.
The calculation of depreciation of vehicles may raise certain questions for the accountant of the organization. The concept of "road transport" includes Cars, trucks, buses, special and other equipment. Legal entities for certain modes of transport can charge depreciation in different ways.
Possible methods of calculating the depreciation of vehicles
Determining the depreciation of fixed assets is the responsibility of a legal entity. Motor transport directly or indirectly participates in the receipt of income by the enterprise, is operated for more than 1 year and costs more than the limit established by law. The procedure for calculating depreciation on it is set out in Accounting Regulations 6/01 and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
How to calculate the useful life of a vehicle?
The next step after choosing a depreciation method is to determine the useful life road transport. It should be understood as the time during which the economic entity will write off the value of the property through depreciation. Organizations are given the right to determine it at their discretion. Moreover, this right extends not only to accounting, but also to tax accounting.
In order to bring tax and accounting records as close as possible, it is recommended that business entities, in order to determine the useful life of vehicles, be guided by the Classification of fixed assets, which is determined by a mandatory document in order to tax accounting.
According to the Classification, vehicles (cars, trucks, buses) are included in different groups. Therefore, the useful life depends on specifications and in which group of the Classification a particular type of vehicle is included.
Most passenger cars and minibuses are included in the third group. The fourth can be attributed to small-class passenger vehicles, and to the fifth - large and higher class.
Determination of the term of use for used machines
In a special order, the term and procedure for calculating depreciation for vehicles purchased in a used condition are determined. In this case, the service life of the machine, established by the Classifier, can be reduced by the time that it was operated by the previous owner.
An important condition is that this period must be confirmed by documents, for example, a vehicle registration certificate. You can also determine the period of operation of the car by the previous owner according to such documents as:
- Transfer-acceptance certificate;
- A certified copy of the object's inventory card.
It is possible that the period of operation of vehicles from the previous owner approaches the upper limit of the period determined by the Classification, or exceeds it. In this case, the new owner can determine the period at his discretion, based on safety requirements and other criteria.
When should a reduction factor be applied?
Legislation establishes the obligation to use a reduction factor when determining the amount of depreciation of vehicles in the event of the purchase of expensive objects. A factor of 0.5 applies to cars, with an initial cost exceeding 600,000 rubles and minibuses more expensive than 800,000 rubles. The obligation to use a reduction factor is established for tax accounting. The legislation in the field of accounting does not establish this need.
Periodically, the limit of the value of the property, for which the reduction coefficient operates, changes. The owners have a question whether such an obligation remains in relation to vehicles, the cost of which has become less statutory values. The question is moot. On the one hand, the chosen method of calculating the depreciation of property should not change throughout the entire period of depreciation. This point of view is shared by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. On the other hand, the presence or absence of a coefficient is not able to change the depreciation method. It follows that in the event of a change in the property value limit, a legal entity - the owner of a vehicle may stop applying the reduction factor. But such a decision, most likely, will have to be defended in court.
When are multipliers applied?
In addition to reducing coefficients, organizations are allowed to use increasing coefficients when calculating the depreciation of vehicles. The need for their application is determined at the initiative of the business entity, depending on the circumstances. Subject to the adoption of a positive decision on the acceleration coefficients, the legal entity is obliged to prescribe this in its internal regulations.
The need to apply a multiplying factor (no more than 2) may arise when vehicles operate in conditions:
- Aggressive environment;
- Increased intensity.
The possibility of applying such a coefficient applies to vehicles received on lease. In this case, the coefficient should not exceed 3. Such a right arises for the lessee, subject to the mutual consent of the parties to the agreement.
Synthetic and analytical accounting of vehicle depreciation
Accrued depreciation of vehicles is included in expenses from ordinary activities. Synthetic accounting of such accruals is kept on passive account 02. The account corresponds with accounts 20, 25, 26, 44, 23, depending on the activity in which the vehicle is operated:
- Dt20 Kt02 - accrued depreciation of the object used in the main activity;
- Dt23 Kt02 - depreciation for vehicles used in auxiliary industries;
- Dt26 Kt02 - depreciation for transport used by management personnel;
- Dt44 Kt02 - depreciation for the transport of a trade enterprise.
From the point of view of tax accounting, the amount of accrued depreciation of vehicles is classified as indirect costs. Companies specializing in providing transport services include these costs as direct costs. Analytical accounting is kept for each unit separately.
Linear method, as the most common
The linear method is the most understandable for an accountant and is universal. The main advantage is the simplicity and the possibility of its application in accounting and tax accounting.
The depreciation rate is calculated by dividing the unit by the useful life and multiplying the result by 100. To calculate the amount of depreciation per month, multiply the monthly rate by the initial cost of the vehicle.
For example, an enterprise truck purchased worth 500,000 rubles. The cost of registration of this vehicle amounted to 500 rubles. Useful life truck is equal to 60 months. The initial cost will be different:
- Accounting - 500000 +500;
- Tax accounting - 500,000.
For the resulting difference, we will form a deferred tax liability (500 * 24% = 120 rubles):
Dt68Kt77. Wear rate:
1/60*100% = 1,67%.
Despite the fact that the depreciation method in accounting and in taxation is the same (linear), its value for the month will be different due to the difference in the initial cost of the truck. In accounting, depreciation:
500500*1.67% = 8358.35. In tax accounting:
500000*1.67% = 8350.00. Monthly postings:
Dt20 Kt02 = 8358.35. Dt77 Kt68 \u003d 2.00 ((8358.35 - 8350) * 24%).
Depreciation of vehicles: other methods of accrual
When determining depreciation by the sum of the numbers of years of useful life, the initial cost of the vehicle is multiplied by the value obtained by dividing the time until the end of its service by the sum of the numbers of years of useful life. The definition of wear is proportional to production due to specificity in relation to cars does not apply.
Answers to current questions
Question #1. The company purchased a car that was previously in operation. According to the new owner, taking into account the condition of the object, its useful life cannot exceed 12 months. How to calculate depreciation in this case?
Answer. In the case when the life of the fixed asset does not exceed 12 months, you can write off its cost immediately in full, without depreciation. But the time of actual operation of the car at the enterprise should not be more than a year.
Question #2.In what cases the legislation allows legal entity stop depreciation?
Answer. The law allows you to suspend depreciation for car case in such cases:
Question #3. Is the registration of a car in the traffic police prerequisite for depreciation? Is it possible to accrue depreciation on a car that has been put into operation, but not registered with the traffic police?
Answer. The basis for the start of depreciation for vehicles, as well as for other fixed assets, is its commissioning. At the same time, registration with the traffic police determines only the right of the car to participate in road traffic, but not at the start of depreciation.
Question #4. Are there any features in the calculation of depreciation of vehicles, determined by its type?
Answer. In general, the algorithm and methodology for calculating the wear and tear of vehicles is the same for different types. But it is worth noting some features:
- To calculate depreciation for passenger cars, it is enough to know the date of production, mileage, guarantee period manufacturer from corrosion;
- For trucks when calculating depreciation, you need to establish the base cost, useful life;
- If depreciation is charged on buses and tractors, then it is important to accurately determine the model and service life;
- When calculating the wear of a special construction equipment the initial cost without the cost of tires is taken into account. Tires are depreciated separately.
Question #5. How is depreciation of a car written off when it is retired?
Answer. The disposal of vehicles is reflected in accounting as follows:
- Dt02 Kt01 - accrued depreciation is written off;
- Dt91 Kt01 - in the amount of the residual value.
Many firms have cars or cars on their balance sheets. passenger minibuses. Let's figure out what is the peculiarity of their depreciation in tax and accounting. How to avoid possible differences between accounts and thus simplify the work of an accountant.
Both in accounting (clause 4 of PBU 6/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n), and in tax accounting (clause 1 of article 257 of the Tax Code), a car is recognized as a fixed asset. Its cost is paid off through depreciation. At linear way The annual depreciation amount is calculated based on the initial cost of the fixed asset, useful life and depreciation rate.
Determine the useful life
When accepting a car for accounting, the company sets its useful life on its own. To do this, determine the expected time of using the car, based on its performance and power (clause 20 PBU 6/01). The possible period of use can also be affected, for example, by the mode and operating conditions.
In tax accounting, the term of use is also set by the company itself, but it must take into account the terms specified in the Classification of fixed assets approved by Government Decree No. 1 of January 1, 2002. To do this, it is necessary to determine which depreciation group the car belongs to (clause 3 of Art. 258 NK). Then establish a specific period of its useful life within the terms specified for this depreciation group.
Calculate the depreciation rate
If in accounting we determine the period of use of the car, for example, 48 months, then the depreciation rate for accounting will be 2.1 percent (100%: 48 months) per month (clause 19 PBU 6/01). Vehicle depreciation is charged starting from the 1st day of the month following the month of acceptance of the object for accounting, and is carried out until the cost is fully repaid or written off (clause 21 PBU 6/01).
If the same period for using the car is determined in tax accounting, then the monthly depreciation rate for tax accounting purposes (clause 4, article 259 of the Tax Code) will be 2.1 percent (1: 48 months x 100%) and will be equal to the rate calculated according to accounting rules. Depreciation starts on the first day of the month following the month in which the car was put into operation (clause 2, article 259 of the Tax Code).
The Tax Code separately allocates expensive cars (clause 9 of article 259 of the Tax Code). He includes cars or minibuses with an initial cost of more than 300 and 400 thousand rubles, respectively. The depreciation rate for such vehicles must be applied with a special coefficient of 0.5.
The procedure for calculating the monthly depreciation rate (for the straight-line method) is as follows: the unit is divided by the useful life in months, and the result is multiplied by 100 percent and by a correction factor of 0.5 (letter of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated February 17, 2005 No. 20 -12/10061). It turns out that for the period of use of vehicles - 48 months, the depreciation rate will be 1.05 percent.
In accounting, there is no such rule and, unlike the tax one, a reduction coefficient cannot be applied (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 21, 2003 No. 16-00-14 / 318).
It turns out that by setting the same period of use of an expensive car in both accounts, the company will actually write it off for tax purposes twice as long. This is possible, since the Tax Code indicates that depreciation on a fixed asset is terminated only if “the initial cost is fully written off or the object has retired from the depreciated property” (clause 2 of article 259 of the Tax Code).
Due to the reduction factor, the monthly depreciation amount in tax accounting will be two times less than in accounting. This will lead to a difference that will have to be taken into account in accordance with the rules of PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax settlements” (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n).
Example
The company has on its balance sheet a passenger car with an initial cost of 480,000 rubles. For simplicity, let's assume that this cost is the same for both accounts.
In accordance with the Classification of Fixed Assets (approved by Government Decree No. 1 of January 1, 2002), cars with an engine capacity of up to 3.5 liters are classified as the third depreciation group. The useful life of such property is from 3 to 5 years inclusive (from 36 to 60 months). Code according to the Classifier - 15 3410010.
The director of the company, both for accounting and for tax accounting, set the period of use of the car - 48 months.
Then for accounting the depreciation rate will be 2.1 percent and monthly it will be possible to write off 10,000 rubles.
For tax accounting purposes, due to the adjustment factor of 0.5, the depreciation rate will be 1.05 percent. As an expense for depreciation, the company will be able to accept only 5,000 rubles. per month.
The amount of expenses that can be taken into account when calculating income tax is 5,000 rubles. less than the amount recognized in accounting. A deductible temporary difference is formed, which leads to the emergence of deferred income tax (subclauses 11, 14 PBU 18/02).
During the first four years, the accountant records:
Debit 09 Credit 68
- 14,400 rubles. (60,000 rubles x 24%) - reflects a deferred tax asset.
Over the next four years, the deductible temporary difference will be canceled and a reverse posting will need to be made. This is due to the fact that in tax accounting depreciation will continue to be charged on this car, while in accounting it will already be depreciated.
Debit 68 Credit 09
- 14,400 rubles. - the deferred tax asset is settled.
As a result, there is no balance on account 09.
Year of depreciation Amount of depreciation in accounting Amount of depreciation in tax accounting Temporary difference (column 2 - colum 3) Deferred tax asset (y. 3 x 24%) 1 2 3 4 5 1st year 120 000 60 000 60 000 14 400 2nd year 120 000 60 000 60 000 14 400 3rd year 120 000 60 000 60 000 14 400 4th year 120 000 60 000 60 000 14 400 5th year – 60 000 -60 000 -14 400 6th year – 60 000 -60 000 -14 400 7th year – 60 000 -60 000 -14 400 8th year – 60 000 -60 000 -14 400
Making life easier for an accountant
To bring together tax and accounting data, a company can set in accounting for expensive cars more long term beneficial use. Just do not forget to indicate this decision in the accounting policy.
If the term is doubled, then the amount of monthly depreciation for accounting purposes will coincide with the monthly amount of depreciation for tax accounting purposes. Then it will not be necessary to apply PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax settlements”.
It should be noted that the proposed option, on the one hand, simplifies accounting and tax accounting (the amount of depreciation will be the same), but, on the other hand, leads to an overestimation of property tax. After all, the basis for this tax is determined according to accounting data (clause 1, article 374 of the Tax Code).
There is one more "but". Since 2006, the company can exercise the right to a depreciation premium (clause 1.1 of article 259 of the Tax Code). This means that in tax accounting, up to 10 percent of the value of the acquired fixed asset put into operation can be written off as expenses at a time. Accounting rules do not provide for this.
In this case, no increase in the useful life of the car in accounting will make the amount of depreciation and accounting according to PBU 18/02 the same for the accountant.
The car was upgraded
A situation is possible when the initial cost of a company car does not exceed 300 thousand rubles. However, later the company decides to modernize it, for example, to install an air conditioner.
In tax accounting, the initial cost of a car increases as a result of modernization (clause 2, article 257 of the Tax Code). If it becomes higher than the cherished three hundred thousand, then from the first day of the month following the month of completion of such modernization, the company will have to halve the depreciation rate.
By the way, in accounting, modernization also increases the initial cost of fixed assets (clause 14 PBU 6/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n).
Voluntary odds
In tax accounting, in addition to the mandatory reduction coefficient, there are voluntary coefficients. The firm decides whether to use them or not. She reflects her decision in the accounting policy.
If the car operates in an aggressive environment or increased shifts, then the company can apply a multiplying factor to the depreciation rate - no higher than 2 (clause 7, article 259 of the Tax Code). For example, if the car is actually used for more than two work shifts (letter of the UMNS for Moscow dated October 2, 2003 No. 26-12 / 54400).
The firm also has the right to apply lower depreciation rates than provided for in articles 258 and 259 of the Tax Code. And this decision should be fixed in the accounting policy for tax purposes.
T. Bursulaia, Senior Auditor, Gradient Alfa Group of Companies Material source -
The entire cost of a vehicle purchased by an enterprise is never written off immediately. It is deducted gradually over the useful life. It is necessary to consider the depreciation of a car in the framework of accounting and tax accounting.
Depreciation of a car is a write-off of the cost of a vehicle in parts in accordance with physical wear and tear. In other words, if the car was purchased by the enterprise, then its cost is not written off by the accounting department immediately, but gradually over several years.
Depreciation deductions relate to the costs of the enterprise. They are deducted from fixed assets (PBU 6/01 of 03/30/2001). This is the cash equivalent of wear and tear.
- the company buys a car;
- the company hires an employee with a car.
Car rental can be recorded on account 01, which reflects information about fixed assets in operation. But only if this asset generates income for more than 12 months in a row.
Depreciation is used in accounting and tax accounting. It is needed to gradually write off the amounts of large expenses so as not to create negative indicators in a short period.
Calculation in accounting
The calculation algorithm is as follows:
- determine the useful life;
- select a calculation method (the direct method is more often used and by the sum of the numbers of the useful life, it can also be calculated with a decrease in the balance or on the basis of machine hours);
- reflect the chosen method in the accounting policy;
- make calculations, apply the chosen method throughout the useful life.
Changing the calculation method is not allowed for an object.
When it is worth starting to write off deductions depends on the period of putting the vehicle into operation, and not the fact of its purchase. It also does not matter when the car was registered with the traffic police.

There are several ways to calculate car depreciation. The basis is the cost of the car without VAT, reflected in the debit of the account. No. 1 "Fixed assets". The money written off is indicated on the credit of account 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets".
The useful life can be peeped in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 1, 2002 No. 1. Cars fall into the 3rd group (3-5 years), 4th (5-7 years), 5th (7-10 years).
For calculations, you can use the directory, which shows the book value of the vehicle model. The resulting value is divided by the period of use and the amount of depreciation is obtained. Not single directory, on which all calculations would line up. As a basis, it is allowed to take nomenclature catalogs published by specialized organizations.
In accounting, two methods are most often used - a linear method and a method based on the sum of useful life numbers. Which of them to apply, chooses the company itself. However, you can stop at a certain option before the commissioning of the accounting object. And you can't change it later.
Line method example
Assumes a uniform write-off of funds over the entire period of depreciation.
For example, the new Ford Transit basic configuration net of VAT costs 1,685 thousand rubles. It is assumed that the enterprise will use it for 5 years (60 months). In this case, the monthly depreciation amount is 28.08 thousand rubles. (337 thousand rubles per year). Total depreciation for each year will be 20%.
For an accurate calculation of deductions taking into account depreciation, it is necessary to take into account the mileage since the beginning of operation, climatic conditions, locality in which the vehicle is to be used, the ecological state of the region. Also important is the brand and country of manufacture of the machine. The quality of the assembly determines how much maintenance and service costs will cost.

An example of a method based on the sum of useful life numbers
Calculation based on the above data of the cost of the car (1,685 thousand rubles). without taking into account the cost of maintaining and servicing the vehicle.
5 years of car operation = 1+2+3+4+5 = 15
First, the serial number of the year of operation is added up: first (1), second (2), third (3), fourth (4), fifth (5), sixth (6). It turns out 15. Then, in the first year of operation, deductions are calculated as follows:
AO = ordinal year (from end) ÷ sum serial numbers years x car cost
T. arr. in the first year, the largest amount is written off, in the last - the smallest.


Depreciation in tax accounting
In tax accounting, a linear and non-linear method is used. With the straight-line method, the amount of annual depreciation is 337 thousand rubles. (1685 ÷ 60). Nonlinear is described in Art. 259.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In tax accounting at the beginning of the reporting period, the organization has the right to change the method of calculation. However, if the non-linear method was initially chosen, then the linear method can be used no earlier than after 5 years.
accelerated depreciation
This is one of the types of depreciation, in which the calculation of depreciation takes place with a multiplying factor - 2 or 3 (Article 259.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Can be applied if the car is leased.