Automatic transmission, also referred to as automatic or chopper, is a type of car transmission that allows you to reduce the load on the driver when driving since gear selection occurs automatically, without driver intervention.
This fact affects all the characteristics of cars with an automatic transmission.




Photo gallery:
- Advantages of automatic transmission
- increasing comfort when driving a car and freeing the driver from control of third-party functions;
- smooth gear shifting and matching the load on the motor with the speed and force of the pedal;
- protection of the motor from any overload; admission to partial or full manual control
transmission.
Types of automatic transmission Automatic boxes modern cars can be divided into several types, differing in the control system and control over the operation of the automatic gearbox. The first type of transmission is controlled using hydraulic device

, and the second – by an electronic distributor.
Types of automatic transmission
The internals of both transmissions are identical, but there are a few layout differences that each automatic transmission has.
We will briefly consider all 3 types of automatic transmissions in more detail in order to understand their differences between each other and the principle of operation.
Types of automatic transmission - briefly about the main thing.
Hydraulic automatic transmission - classic automatic transmission The hydraulic type of automatic transmission is the simplest automatic transmission. Such a box eliminates direct connection between the engine and wheels. The torque in it is transmitted by two turbines and working fluid. Due to the improvement of the mechanism, specialized electronic device
, which was also able to add such operating modes as: “winter”, “sport”, economical driving.
One of the main disadvantages, in comparison, is slightly higher fuel consumption and acceleration time.
Robotic automatic transmission MTA popularly sounds like robot DSG , structurally most similar to a manual transmission, but from a control point of view - typical automatic transmission
, which, as a result of evolution, not only reduces fuel consumption, but also a number of other advantages, naturally with their own nuances.
Although considered an automatic transmission, they are fundamentally different both in design and operating principle. There are no steps in such a gearbox since there is no fixed gear ratio. Drivers who are accustomed to listening to the engine of their car cannot monitor its operation, because the torque in the variator box changes smoothly and the engine tone does not change.
Automatic transmission components
- torque converter, which replaces the clutch and does not require participation and control by the driver.
- installed instead of a gear block in the automatic transmission planetary gear. This part helps change the attitude in the automatic transmission when shifting the transmission.
- front and rear clutch, as well as a brake band, thanks to which gear shifting is carried out directly.
- The last and most important detail is control device, which is a unit consisting of a transmission pan, a pump and a valve box that performs control functions. This component transmits movement data through signs that transmit a signal to the automatic transmission itself.
Design and operation of an automatic transmission.
Of all the main components, we will pay the most attention to the torque converter of the box.
The torque converter includes:
- centrifugal pump;
- stator;
- centripetal turbine;
- pump wheel;
- turbine wheel;
The stator is a guide device that is located between these parts. The pump wheel is connected to the engine crankshaft, and the turbine wheel is connected to the gearbox shaft. The reactor has 2 functions. It can rotate or be locked by the overrunning clutch.
The main task of the torque converter is to dampen strong shocks that are transmitted by the transmission to the engine and in the opposite direction. This device increases the service life of these parts. With help liquid oil torque is transmitted from the engine to the automatic transmission.
In order for the automatic transmission to work for a long time and properly, it is necessary to regularly undergo diagnostics at a service station.
Pay attention to the following details:
- gears must be changed in 1 second, maximum time - 1.5 seconds;
- notification of switching is carried out by light jolts;
- Gear shifting should be silent.
How does an automatic transmission work?
In a hydromechanical automatic transmission in the classic version, gear shifting occurs due to the interaction of planetary mechanisms and a hydromechanical drive using electronic devices.
How to use it correctly classic automatic transmission?
Features of automatic transmission operation
- Automatic transmission needs to be warmed up well before you start driving (this is especially important in winter).
- When driving an automatic transmission, translate selector lever in positions P and R while driving, urgently Not recommended.
- No need to enable neutral gear during the descent from the mountain, supposedly fuel economy, - it won’t happen anyway, but problems with braking may arise.
- Engine braking is not possible in all gearbox modes. This operating point must be studied in detail in the operating manual. specific car, neglecting such a feature can cost expensive repairs.
Automatic transmission problems and solutions
The most common automatic transmission problems are considered to be:
- a pronounced jerk when changing gears, as well as noise when moving the selector lever to another position;
- quite often in automatic transmissions the brake bands of the front and rear clutches break;
- failure of the electrical or hydraulic unit.
With the development of the automotive industry and the release of new types of transmissions, the question of which gearbox is better is becoming increasingly relevant. Automatic transmission - what is it? In this article, we will understand the structure and operating principle of an automatic transmission, find out what types of automatic transmissions exist and who invented the automatic transmission. Let's analyze the advantages and disadvantages different types automatic transmissions. Let's get acquainted with the operating and control modes of the automatic transmission.
What is automatic transmission and the history of its creation
Automatic transmission selectorAutomatic transmission gears, or automatic transmission, is a transmission that allows the selection of the optimal gear ratio in accordance with driving conditions without driver intervention. This ensures a good smooth ride of the car, as well as driving comfort for the driver.
Currently, there are several types of automatic transmission:
- hydromechanical (classical);
- mechanical;
This article will focus on classic slot machine.
History of invention
The basis of the automatic transmission is a planetary gearbox and a torque converter, first invented exclusively for the needs of shipbuilding in 1902 by the German engineer Hermann Fittenger. Then, in 1904, the Startevent brothers from Boston presented their version of an automatic transmission, which had two gearboxes and resembled a slightly modified mechanics.
 First production GM Hydramatic automatic transmission
First production GM Hydramatic automatic transmission A car equipped with a planetary gearbox first saw the light of day under Ford brand T. The essence of the box was to smoothly change gears using two pedals. The first included upshifts and downshifts, and the second included reverse gears.
The company took up the baton General Motors, which introduced a semi-automatic transmission in the mid-1930s. The clutch was still present in the car, and the planetary mechanism was controlled by hydraulics.
Around the same time, Chrysler refined the design of the gearbox with a fluid coupling, and instead of a two-stage gearbox, overdrive was used - an overdrive gear with a gear ratio of less than one.
The world's first fully automatic transmission was created in 1940 by the same company, General Motors. The automatic transmission was a combination of a fluid coupling with a four-speed planetary gearbox with automatic control through hydraulics.
Today, six-, seven-, eight- and nine-speed automatic transmissions are already known, the manufacturers of which are both automakers (KIA, Hyundai, BMW, VAG) and specialized companies (ZF, Aisin, Jatco).
Pros and cons of automatic transmission
Like any transmission, automatic transmission has both pros and cons. Let's present them in the form of a table.
Automatic transmission device
 Automatic transmission diagram
Automatic transmission diagram The automatic transmission device is quite complex and consists of the following main elements:
- planetary mechanism;
- automatic transmission control unit (TCU);
- hydraulic unit;
- band brake;
- oil pump;
- frame.
The torque converter is a housing filled with a special working ATF fluid, and is designed to transmit torque from the engine to the gearbox. In fact, it replaces the clutch. It consists of a pump, turbine and reactor wheels, a locking clutch and a coupling freewheel.
The wheels are equipped with blades with channels for passage working fluid. A lock-up clutch is necessary to lock the torque converter in specific vehicle operating modes. A freewheel (overrunning clutch) is necessary to rotate the reactor wheel in the opposite side. You can read more about the torque converter.
The planetary mechanism of the automatic transmission includes planetary gears, shafts, drums with friction clutches, as well as an overrunning clutch and a band brake.
The gear shift mechanism in an automatic transmission is quite complex, and, in fact, the operation of the transmission consists of executing some algorithm for turning the clutches and brakes on and off using fluid pressure.
The planetary gear, or more precisely the locking of one of its elements (sun gear, satellites, ring gear, carrier), ensures the transmission of rotation and changes in torque. The elements included in the planetary gear are locked using an overrunning clutch, a band brake and friction clutches.
 An example of an automatic transmission hydraulic diagram
An example of an automatic transmission hydraulic diagram The automatic transmission control unit can be hydraulic (no longer used) and electronic (automatic transmission control unit). Modern hydromechanical transmission equipped only with an electronic control unit. It processes sensor signals and generates control signals to the actuators (valves) of the valve body, which ensure the operation of friction clutches, as well as control the flow of working fluid. Depending on this, fluid under pressure is directed to one or another clutch, including a specific gear. The TCU also controls the torque converter lock-up. In the event of a malfunction, the TCU ensures that the gearbox operates in " emergency mode" The automatic transmission selector is responsible for switching gearbox operating modes.
The following sensors are used in the automatic transmission:
- input speed sensor;
- output speed sensor;
- automatic transmission oil temperature sensor;
- selector lever position sensor;
- oil pressure sensor.
Operating principle and service life of automatic transmission
The time required to change speed in an automatic transmission depends on the speed of the vehicle and the load on the engine. The control system calculates necessary actions and transmits them in the form of hydraulic influences. Hydraulics move the clutches and brakes of the planetary mechanism, thereby automatically changing the gear ratio in accordance with the optimal engine mode under given conditions.
One of the main indicators affecting the efficiency of an automatic transmission is the oil level, which must be checked regularly. Working temperature oil (ATF) is about 80 degrees. Therefore, in order to avoid damage to the plastic mechanisms of the box in winter period, the car must be warmed up before driving. And in the hot season, on the contrary, cool it.
The automatic transmission can be cooled by coolant or air (using an oil cooler).

Most widespread Got a liquid radiator. Temperature atf required for normal engine operation should not exceed 20% of the temperature in the cooling system. The coolant temperature should not exceed 80 degrees, due to this the atf is cooled. The heat exchanger is connected to the outer part of the oil pump housing, to which the filter is attached. As oil circulates in the filter, it comes into contact with the cooling liquid through the thin walls of the channels.
By the way, automatic transmission is considered very heavy. The weight of the automatic transmission is about 70 kg (if it is dry and without a torque converter) and about 110 kg (if it is filled).
For normal operation of the automatic transmission, it is necessary and correct pressure oils The service life of the automatic transmission largely depends on this. The oil pressure should be between 2.5-4.5 bar.
The resource of an automatic transmission may vary. If in one car the transmission can last only 100 thousand km, then in another it can last about 500 thousand. This depends on the operation of the car, on regular monitoring of the oil level and its replacement along with the filter. It is also possible to extend the life of an automatic transmission using original Consumables and timely servicing the checkpoint.
Automatic transmission control
The automatic transmission is controlled by the automatic transmission selector. The operating modes of the automatic transmission depend on moving the lever to a certain position. The following modes are available in the machine:
- R - Parking. Used when parking. IN this mode The transmission output shaft is mechanically blocked.
- R - Reverse. Used to engage reverse gear.
- N - Neutral. Neutral mode.
- D – Drive. Moving forward in automatic gear shift mode.
- M - Manual. Mode manual switching speeds
In modern automatic transmissions with a large number of operating ranges, they can be used additional modes works:
- (D), or O/D-overdrive - “economical” driving mode, in which it is possible automatic switching to overdrive;
- D3, or O/D OFF - stands for “disabling overdrive”, this is the active driving mode;
- S(or number 2 ) - range of low gears (first and second, or only second gear), " winter mode»;
- L(or number 1 ) - second range of low gears (first gear only).
 Automatic transmission mode diagram
Automatic transmission mode diagram There are also additional buttons, characterizing the operating modes of the automatic transmission.
ARTICLE VIDEO How does an automatic transmission work? What are all the advantages and delights of driving a car with an automatic transmission, how reliable and durable is the automatic transmission, what can and cannot be done if you have an automatic transmission, and is the automatic transmission really as “dumb” as they say, or can it “do the job”? » the car on the mechanics and leave it far behind? Read in this article!
Automatic transmission device
The automatic transmission consists of several main components:
Arrangement of elements in the automatic transmission box:

Planetary gear system
 The heart of the automatic transmission is the planetary mechanism.
The heart of the automatic transmission is the planetary mechanism.
Planetary gears have 3 degrees of freedom. This means that in order to transmit rotation, one of the 3 elements (satellites do not count) must be stopped.
If you do not stop any of the elements, then each will be able to move freely, and in this case there will be no transmission of rotation.
You can brake other elements, as well as swap entry and exit points, obtaining different gear ratios and return directions rotation.
Wherein external dimensions designs will change slightly. Such properties determined the use of planetary mechanisms in automatic transmissions.
Automatic transmission, short video on the device:
Torque converter
 A torque converter is used to transmit torque from the automatic transmission to the engine. In fact, it performs almost the same functions as the clutch in mechanics.
A torque converter is used to transmit torque from the automatic transmission to the engine. In fact, it performs almost the same functions as the clutch in mechanics.
In addition, it can increase torque by reducing the reactor's fluid flow rate.
Operating principle of the torque converter:
The torque converter consists of three main elements.
These are two blades, one on the gearbox side, the other on the engine side. Between them is the so-called reactor. All these three parts are not mechanically connected to each other; they are in a special liquid.
When the blades connected to the engine rotate, torque is transmitted through liquid to the blades connected to the box, and the box begins to work.
The geometric characteristics of the torque converter blades and cross-sections are selected in such a way that at rpm idle move The torque transmitted from the engine is very small and can be countered even by lightly pressing the brake pedal.

However, a slight press on the gas pedal and a slight increase in speed causes a significant increase in the transmitted torque.
This happens because as the engine speed increases, the direction of the fluid flow changes in the direction of increasing pressure on the turbine blades

Torque converters modern automatic transmissions can increase the torque transmitted from the engine by two to three times. This effect only occurs when the crankshaft rotates significantly faster than the automatic transmission input shaft.
As the car picks up speed, this difference decreases and a moment comes when the input shaft rotates at almost the same speed as the crankshaft, but not exactly, since the transmission of torque from the engine to the automatic transmission is carried out through liquid, i.e. with slippage.
This is part of the explanation why cars with automatic transmission are less economical and dynamic rather than exactly the same ones with manual transmission.
To minimize these losses, torque converters are equipped with locking devices. When angular velocities the impeller and turbine are aligned, the locking connects them into a single unit, eliminating slippage.

To connect the elements of the planetary mechanism to input shaft The boxes automatically use clutches and brakes to stop them relative to the body. Both of them are most often multi-disc clutches.

Hydraulic system
Working fluid in the automatic transmission hydraulic system - ATF oil, provides lubrication, cooling, gear shifting and connection of the transmission to the engine. As a rule, the oil in the box is in the crankcase.
Because The oil volume changes during automatic transmission operation; it is connected to atmospheric air through a dipstick.
As source of pressure in the automatic transmission internal gear pumps are used. The advantage of internal gear pumps is that high power pump, especially at low speeds.
October 23, 2016A car's automatic transmission is designed to transfer engine power to the wheels. It selects exactly the gear that is best suited for the current speed. Automatic transmission eliminates the need for the driver to manually change gears. The car's computer, using sensors, determines at what point it is necessary to change gear and sends a signal electronically to engage or disengage the gear.
Basic elements of an automatic transmission
A car's automatic transmission is a system of levers and gears that transfer power to the drive wheels, allowing the engine to operate at its most efficient.
The box is assembled in an aluminum casing called a crankcase. It contains the main components of the automatic transmission:
- A torque converter that acts as a clutch, but does not require direct control by the driver.
- Planetary gear that changes the gear ratio when switching.
- Rear, front clutches, brake band, which directly carry out gear shifting.
- Control device.
How does a torque converter work?
The torque converter consists of the following main elements:
- pump or pump wheel;
- turbine wheel;
- blocking plates;
- stator;
- overrunning clutch.

To understand how an automatic transmission works, you need to understand its structure in general. Thus, the pump is connected to the engine by a mechanical connection. The turbine wheel is connected to the gearbox shaft using splines. When the pump wheel rotates while the engine is running, an oil flow is created, which rotates the turbine wheel of the torque converter.
In this case, the torque converter plays the role of a regular fluid coupling, only transmitting torque from the engine to the automatic transmission shaft through liquid. As engine speed increases, there is no significant increase in torque.
To convert torque, the automatic transmission circuit includes a stator. The principle of operation is that it redirects the flow of oil back to the pump impeller, causing it to rotate faster, increasing torque. The lower the speed of rotation of the turbine wheel relative to the pump, the greater the residual energy transferred by the stator through the return oil to the pump. Accordingly, the torque increases.
Basics of operation of the turbine and automatic transmission pump
The turbine always rotates slower than the pump. The maximum ratio of pump and turbine rotation speeds is achieved when the vehicle is stationary, decreasing as the speed increases vehicle(TS). The stator is connected to the torque converter through an overrunning clutch that can only rotate in one direction.
The turbine and stator blades have a special shape, due to which the oil flow is redirected to reverse side stator blades. In this case, the stator jams and, remaining motionless, transfers the greatest oil energy to the pump input.

Due to this mode of operation of the torque converter, maximum torque transmission is ensured. It increases almost three times when the car starts moving.
As the vehicle accelerates, the turbine slips less and less relative to the pump until the moment when the stator wheel is picked up by the oil flow and begins to rotate in the direction of the freewheel of the overrunning clutch. In this case, the device begins to work like a regular fluid coupling and does not increase torque. In this mode, the efficiency of the torque converter does not exceed 85%. This mode of operation is accompanied by the release of excess heat and increased fuel consumption.
Purpose of the blocking plate
This drawback is eliminated using special device- blocking plate. Despite the mechanical connection with the turbine, it is structurally designed in such a way that it can move left and right. This device is activated when the vehicle reaches high speed. Upon command from the control device, the oil flow changes so that it presses the locking plate against the torque converter housing on the right.
In this case, the turbine and pump are connected to each other mechanically. To increase grip inner side A special friction layer is applied to the torque converter housing. In this way, the engine is connected to the output shaft of the automatic transmission. Naturally, such a lock is immediately turned off even with slight braking of the car.
Only one method of locking a torque converter was described above. However, any other method serves the same purpose - to prevent the turbine from slipping relative to the pump wheel. Typically, the described mode of action in various sources is called Lock-Up.
It will be easier to understand the operation of a torque converter for dummies if, instead of a turbine and a pump, we imagine two simple fans, one of which operates from the mains, and the other rotates due to created first air flow fan. Only instead of air, oil appears here, and the blades of the first fan (pump in the case of an automatic transmission) are driven not by electricity, but by a mechanical connection to the car’s engine shaft.
Planetary series
The torque converter can increase torque, but only up to a certain limit. Design of an automatic transmission for a more significant increase in torque, for example when climbing hills, as well as for driving in reverse provides planetary gears. The planetary gear also ensures smooth gear shifting when driving without loss of engine power. Thanks to it, switching occurs without the shocks that occur during operation of a conventional transmission.

The planetary set includes the following elements:
- sun gear;
- satellites;
- epicycle;
- drove.
They are called a planetary gear due to the fact that friction wheels, rotating simultaneously around their axes and moving with these axes, are very reminiscent of the planets of the solar system. Their mutual position determines which this moment gear is on.
How do gears change in an automatic transmission?
Shifting gears or changing the gear ratio in the planetary gearbox is carried out by locking and unlocking the planetary gear elements using brake bands and clutches. IN hydraulic system In an automatic transmission of a car, gear shifting is carried out directly by a valve. The three-speed gearbox has two such valves, one of which switches from first to second gear, the other from second to third. The four-speed gearbox already has three valves.
Other types of automatic transmission
In addition to the discussed hydraulic transmission Today, other types of automatic transmissions are widespread:
- CVT automatic transmission. In this type of transmission there is no fixed ratio for the gears. Therefore, such an automatic transmission is called continuously variable. The operating principle is that, unlike other automatic machines, it uses engine power more efficiently. As a result, cars equipped with this type of transmission are more economical and comfortable.
- Robotic gearbox. Such a box can be called automatic, conditionally, since in essence it is an ordinary “mechanics”, where the function of the clutch pedal is assigned to the electronic unit. Cars with which gearboxes are also quite economical, but less comfortable, since gear shifts are often automatic mode accompanied by jerking.
Thus, in addition to the most common hydraulic automatic transmission, there are several types of automatic transmissions that differ in their design. They differ in price, efficiency, and driving comfort. The general thing is that the driver is relieved of the need independent choice and gear shifting.
An automatic transmission has a number of undeniable advantages. It greatly simplifies driving. Shifts are made smoothly, without jerking, which improves ride comfort and increases the service life of the transmission. Modern automatic transmissions have the ability to manually change gears and operating modes, and can adapt to the driving style of a particular driver.
But even the most perfect hydromechanical boxes are not without shortcomings. These include: design complexity, high price and maintenance costs, lower efficiency, worse dynamics and increased consumption fuel consumption compared to a manual transmission, slower shifts.
An automatic transmission consists of the following main components: torque converter, planetary gear, control and monitoring system. Box front wheel drive cars additionally contains the main gear and differential inside the housing.
To understand how an automatic transmission works, you need to understand what a fluid coupling and planetary gear are. Fluid coupling is a device consisting of two impellers installed in one housing, which is filled with special oil. One of the wheels, called the pump wheel, is connected to the engine crankshaft, and the second, the turbine wheel, is connected to the transmission. When the pump wheel rotates, the oil flows it throws spin the turbine wheel. This design allows torque to be transmitted in approximately a 1:1 ratio. This option is not suitable for a car, since we need the torque to vary over a wide range. Therefore, between the pump and turbine wheels they began to install another wheel - a reactor wheel, which, depending on the mode of movement of the car, can be either stationary or rotating. When the reactor is stationary, it increases the flow rate of the working fluid circulating between the wheels. The higher the speed of the oil, the greater the impact it has on the turbine wheel. Thus, the torque on the turbine wheel increases, i.e. we transform it. Therefore, a device with three wheels is no longer a fluid coupling, but a torque converter.
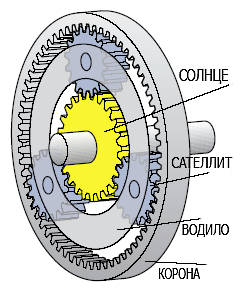
But the torque converter cannot convert the rotation speed and transmitted torque within the limits we need. Yes, and he is not able to provide reverse movement. Therefore, a set of separate planetary gears with different gear ratios is attached to it - like several single-stage gearboxes in one housing. A planetary gear is a mechanical system consisting of several gears - satellites - rotating around a central gear. The satellites are fixed together using a carrier. The outer ring gear has internal mesh with the planetary gears. The satellites mounted on the carrier rotate around the central gear, like planets around the Sun (hence the name planetary gear), the outer gear rotates around the satellites. Different gear ratios are achieved by fixing various parts relative to each other.
Gear shifting is carried out by a control system that early models was completely hydraulic, and on modern ones electronics came to the aid of hydraulics.
Torque converter operating modes
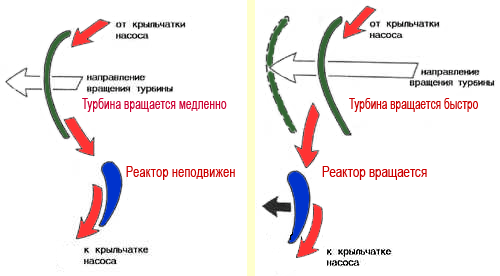
Before movement begins, the pump wheel rotates, the reactor and turbine wheels are stationary. The reaction wheel is fixed to the shaft using a freewheel and therefore can only rotate in one direction. We switch on the gear, press the gas pedal - the engine speed increases, the pump wheel picks up speed and spins the turbine wheel with flows of oil. The oil thrown back by the turbine wheel hits the stationary blades of the reactor, which additionally “twist” the oil flow, increasing its kinetic energy, and direct it to the blades of the pump wheel. Thus, with the help of the reactor, the torque is increased, which is what is required when accelerating the car. When the car has accelerated and is moving at a constant speed, the pump and turbine wheels rotate at approximately the same speed. In this case, the flow of oil from the turbine wheel hits the reactor blades on the other side, due to which the reactor begins to rotate. There is no increase in torque; the torque converter switches to fluid coupling mode. If the resistance to the movement of the car has increased (for example, the car is going uphill), the rotation speed of the drive wheels, and, accordingly, the turbine wheel, decreases. In this case, the oil flows again stop the reactor - the torque increases. In this way, the torque is automatically adjusted depending on the driving mode.
The absence of a rigid connection in the torque converter has its advantages and disadvantages. Pros: torque changes smoothly and steplessly, torsional vibrations and jerks transmitted from the engine to the transmission are damped. Disadvantages - low efficiency, since part of the energy is lost when “shovelling the oil” and is spent on driving the automatic transmission pump, which ultimately leads to increased fuel consumption.
To eliminate this drawback, the torque converter uses a locking mode. When the driving mode is established in higher gears, it automatically turns on mechanical locking wheels of the torque converter, that is, it begins to perform the function of a conventional “dry” clutch. This ensures a rigid direct connection between the engine and the drive wheels, as in mechanical transmission. On some automatic transmissions, the inclusion of the locking mode is also provided for lower gears. Driving with locking is the most economical operating mode of the automatic transmission. When the load on the drive wheels increases, the locking is automatically switched off.
When the torque converter operates, the working fluid heats up significantly, so the automatic transmission design includes a cooling system with a radiator, which is either built into the engine radiator or installed separately.
How does a planetary gear work?
Why do automatic transmissions in the vast majority of cases use planetary gears, and not shafts with gears, as in mechanical box? The planetary gear is more compact and provides faster and smoother gear changes without interruption in engine power transmission. Planetary gears are durable because the load is transmitted by several planets, which reduces tooth stress.
In a single planetary gear, torque is transmitted using any (depending on the selected gear) two of its elements, one of which is the driving element, the second is the driven one. The third element is motionless.
To obtain direct transmission, it is necessary to fix any two elements together that will play the role of a slave link; the third element, when connected in this way, is the master. The general gear ratio of such gearing is 1:1.
Thus, one planetary gear can provide three forward gears (reduction, direct and overdrive) and reverse gear.
The gear ratios of a single planetary gear set do not allow for optimal use of engine torque. Therefore, it is necessary to combine two or three such mechanisms. There are several connection options, each of which is named after its inventor.
Simpson planetary gear, consisting of two planetary gearboxes, is often called a double row. Both groups of satellites, each of which rotates inside its own ring gear, are combined into a single mechanism by a common sun gear. A planetary gearset of this design provides three stages of change gear ratio. To obtain the fourth, overdrive gear, another planetary gear is installed in series with the Simpson row. Simpson's scheme found greatest application in automatic transmission for rear wheel drive cars. High reliability and durability with relative simplicity of design - these are its undeniable advantages.
Planetary series Ravigneux sometimes called one-and-a-half, emphasizing the features of its design: the presence of one ring gear, two sun gears and a carrier with two groups of satellites. The main advantage of the Ravigneux scheme is that it allows you to obtain four stages of changing the gear ratio. The absence of a separate planetary overdrive gear makes the gearbox very compact, which is especially important for transmissions of front-wheel drive vehicles. The disadvantages include a reduction in the service life of the mechanism by approximately one and a half times compared to the Simpson planetary gear. This is due to the fact that the gears of the Ravigneux transmission are constantly loaded in all operating modes of the box, while the elements of the Simpson series are not loaded while driving in high gear. The second drawback is the low efficiency at lower gears, leading to a decrease in the acceleration dynamics of the car and the noise of the gearbox.
Wilson gearbox consists of 3 planetary gearboxes. The ring gear of the first planetary gearbox, the carrier of the second gearbox, and the ring gear of the third are constantly connected to each other, forming a single whole. In addition, the second and third planetary gearboxes have a common sun gear, which drives the gears forward travel. Wilson's design provides 5 forward gears and one reverse gear.
Planetary gear Lepeletje combines an ordinary planetary gear and the Ravinier planetary gear docked behind it. Despite its simplicity, such a box provides 6 forward gears and one reverse gear. The advantage of the Lepeletye scheme is its simple, compact and light-weight design.
Designers are constantly improving automatic transmissions, increasing the number of gears, which improves the smooth operation and efficiency of the car. Modern automatic transmissions can have up to eight gears.
How does the automatic transmission control system work?
There are two types of automatic transmission control systems: hydraulic and electronic. Hydraulic systems are used on outdated or budget models, modern automatic transmissions are controlled electronically.
The “life support” device for any control system is the oil pump. It is driven directly from the engine crankshaft. The oil pump creates and maintains constant pressure in the hydraulic system, regardless of the crankshaft speed and engine load. If the pressure deviates from the nominal value, the operation of the automatic transmission is disrupted due to the fact that actuators Gear shifts are controlled by pressure.
Gear shift timing is determined by vehicle speed and engine load. To do this in hydraulic control system There are two sensors: a speed regulator and a valve - throttle or modulator. A speed pressure regulator or hydraulic speed sensor is installed on the output shaft of the automatic transmission. The faster the car goes, the more the valve opens, the greater the pressure passing through this valve. transmission fluid. Designed to determine the load on the engine, the throttle valve is connected by a cable or throttle valve(V gasoline engines), or with the injection pump lever (in diesel engines).
In some cars, to apply pressure to the throttle valve, it is not a cable that is used, but a vacuum modulator, which is driven by vacuum intake manifold(as the load on the engine increases, the vacuum drops). Thus, these valves generate pressures proportional to the vehicle speed and engine load. The ratio of these pressures makes it possible to determine the moments of gear shifting and torque converter locking. The range selection valve, which is connected to the automatic transmission selector lever and, depending on its position, prohibits the inclusion of certain gears, is also involved in the “decision-making” of gear shifting. The resulting pressure created by the throttle valve and speed controller causes the corresponding switch valve to operate. Moreover, if the car accelerates quickly, the control system will engage an upshift later than during quiet acceleration.
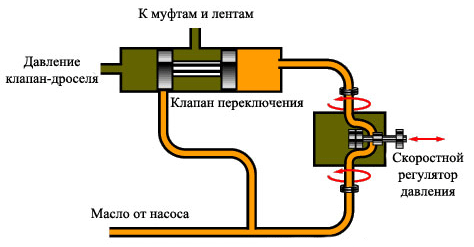
How does this happen? The switching valve is under oil pressure from the high-speed pressure regulator on one side and from the throttle valve on the other. If the car accelerates slowly, pressure from the hydraulic speed valve builds, causing the shift valve to open. Since the accelerator pedal is not fully depressed, the throttle valve does not create much pressure on the shift valve. If the car accelerates quickly, the throttle valve creates more pressure on the shift valve, preventing it from opening. To overcome this resistance, the pressure from the speed regulator must exceed the pressure from the throttle valve, but this will happen when the car reaches a higher speed than during slow acceleration.



Each shift valve corresponds to a certain pressure level: the faster the car moves, the more top gear will turn on. The valve block is a system of channels with valves and plungers located in them. Shift valves supply hydraulic pressure to the actuators: friction clutches and brake bands, through which the various elements of the planetary gear are locked and, therefore, switched on (off) various gears. A brake is a mechanism that locks the elements of the planetary gear set onto the stationary body of the automatic transmission. The friction clutch blocks the moving elements of the planetary gearset among themselves.
Electronic control system just like hydraulic, it uses two main parameters for operation: vehicle speed and engine load. But to determine these parameters, not mechanical, but electronic sensors. The main ones are sensors: speed at the input of the gearbox, speed at the output of the gearbox, temperature of the working fluid, position of the selector lever, position of the accelerator pedal. In addition, the automatic transmission control unit receives Additional information from the engine control unit and other electronic systems of the car (for example, from ABS). This allows you to more accurately determine the moments of switching and locking of the torque converter than in a conventional automatic transmission. The gear shift program, based on the nature of the speed change at a given engine load, can easily calculate the force of resistance to vehicle movement and introduce appropriate amendments to the shift algorithm, for example, turn it on later overdrive in a fully loaded vehicle.
Electronically controlled automatic transmissions, like simple hydromechanical transmissions, use hydraulics to operate the clutches and brake bands, but each hydraulic circuit is controlled by a solenoid valve rather than a hydraulic valve.
The use of electronics has significantly expanded the capabilities of automatic transmissions. They received various modes works: economical, sports, winter. The sharp increase in the popularity of automatic transmissions was caused by the advent of the Autostick mode, which allows the driver to independently select the desired gear. Each manufacturer gave this type of gearbox its own name: Audi – Tiptronic, BMW – Steptronic. Thanks to electronics in modern automatic transmissions, the possibility of their “self-learning” has become available, i.e. changing the switching algorithm depending on driving style. Electronics provided ample opportunities for automatic transmission self-diagnosis. And it's not just about memorizing fault codes. The control program, monitoring the wear of friction discs and oil temperature, makes the necessary adjustments to the operation of the automatic transmission.
Automatic transmission malfunctions
Malfunctions in the operation of automatic transmissions most often manifest themselves in sluggish acceleration, jerks during shifts, failure to engage one or more gears, erratic shifting, extraneous noise at work. The cause of many operational problems is insufficient oil level in the box. On most cars, the procedure for checking it is the same. Having placed the car on a level surface, with the engine running and the brake pedal pressed, turn on all modes one by one for a few seconds. This allows the oil to spread throughout all channels. After this, we install the automatic transmission selector, depending on the specific brand, or in neutral position, or to the parking position. We take out the dipstick and check the level. There may be two marks on the dipstick - minimum and maximum level, or four - two for cold oil, two for warm oil.
For some brands, the verification procedure differs from that described above. For example, on Honda automatic machines the oil level is checked at engine not running. Not all boxes have probes, but may only have a control hole closed with a plug. In this case, the level is checked with a “service” dipstick, which is only available in the workshop. To check the level, a control plug in the pan can also be used.
In some cars, the main gear uses not cylindrical, but bevel hypoid gears, which are lubricated by transmission oil. Therefore, if the gears are located in the same housing with the automatic transmission clutches, a separate crankcase is used for oil. When topping up, it is important not to mix up the plugs, since the oils for the box and final drive, naturally, are incompatible.
At insufficient level you can hear oil from the box extraneous sounds, the oil pump begins to make noise. Overwatering is also harmful - excess oil foams, undergoes overheating and oxidation. The excess can be easily pumped out using a syringe with a flexible tube attached to it.
After checking the level in mandatory you should evaluate the condition of the oil - its color and smell. Normal operating oil should be dark brown or dark red in color and not have a burning smell. It should be fluid and not sticky. Mechanical impurities and cloudiness indicate the presence of malfunctions. Impurities enter the oil as a result of wear of box parts. Cloudiness is caused by antifreeze if oil radiator The automatic transmission is built into the engine cooling radiator. In addition, friction clutches, absorbing antifreeze, swell and lose their properties. If the oil has a burning smell, this is a sure sign that the clutches are burning. Difficult conditions operation leads to overheating of the oil, and it becomes discolored. If the color and smell of the oil are normal, then its level is restored by topping up, but if the oil is unsuitable, it is replaced with mandatory replacement And oil filter. It is also recommended to change the oil after 120-150 thousand kilometers, even if the manufacturer promises its use throughout the entire service life of the box.
One of the most important details Automatic transmission - pump. They are of gear or blade type. The pump creates the pressure necessary for the box to operate. If the oil level is insufficient, air enters the system. As the air is compressed, the pressure in the hydraulic system drops. As a result, gears are switched late, clutches slip and wear out faster. Damage to the sump can also lead to malfunctions of the pump. If the car hit the bottom, after which a loud noise appears, check the pan first. A deformed part interferes with normal oil pumping.
If there are disturbances in the operation of the box, but the oil level and its quality are normal, more serious diagnostics are necessary. Electronics are the most capricious and unpredictable part of an automatic transmission. All modern boxes have their own control unit, which records errors in its operation. But scanners capable of reading full information, are available only from official dealers. However, some ECUs have an “advanced” self-diagnosis system, which simplifies the work of a specialized service diagnostician. But finding a good diagnostician is not easy. After all, he must not only know how the automatic transmission works, but also how it interacts with the engine control system. For example, due to a sensor malfunction mass flow air on some cars may reduce the oil pressure in the automatic transmission. As a result, the clutches “slip”, and an inexperienced specialist will look for a fault in the box itself for a very long time. A good diagnostician must have analytical skills, because engineers are constantly improving automatic transmission designs, introducing new sensors and actuators. Repair documentation does not always reflect these changes; the service specialist has to figure them out on his own.
In addition, temporary malfunctions may occur in the operation of a completely serviceable box. For example, in dense city traffic, the electronics, overheating, begin to randomly switch from first to second gear and vice versa. As soon as driving conditions become more uniform, the operation of the automatic transmission returns to normal. The same illogical behavior can be provoked by a “sporty” driving style. The owner contacts the service center with a complaint, but the diagnostician does not find any errors in the ECU memory!
Another important node any automatic transmission is a torque converter. It plays the role of a clutch, transmitting torque from the engine. Its most common malfunctions are breakdown of the reactor freewheel and wear of the thrust bearings. When the clutch fails, the torque transmitted by the torque converter drops, and vehicle acceleration becomes slow. Wear thrust bearing is manifested by increased noise when the selector is positioned in all “driving” modes and its disappearance in the “neutral” and “parking” positions. Severe wear can cause the turbine wheel and pump wheel to cling to each other, and bending of their blades is inevitable.
In general, during any automatic transmission repair, the torque converter must be opened for preventive maintenance. This work is carried out by highly qualified specialists. The torque converter is secured and opened along the weld seam. Adjustment of bearing clearances and final welding during assembly require special skill.